Water Rights Conflicts Between States: Causes & Consequences – Lichcupdienevn.com. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding the Causes of Water Rights Conflicts Between States
Water rights are a fundamental aspect of our society, governing how we use and manage this vital resource. Over the years, water rights systems have evolved, with two major doctrines emerging: riparian rights and prior appropriation. Riparian rights grant water use rights to landowners along a watercourse, while prior appropriation awards rights to the first user who appropriates water for a beneficial use. These systems can create conflicts, especially when water is scarce.
The increasing demand for water, driven by population growth and urbanization, puts immense pressure on existing resources. Moreover, climate change and drought are exacerbating water scarcity, leading to competition for limited supplies. Agriculture and industry further contribute to the demand for water, creating a complex web of needs and priorities.
States prioritize water use for different purposes, such as agriculture, urban development, and industrial production. These competing interests can lead to disagreements over how to allocate limited water resources. The absence of clear water rights agreements further complicates the situation. Ambiguous or incomplete interstate compacts, disputes over the interpretation of existing agreements, and the lack of comprehensive water management planning can all escalate conflicts.
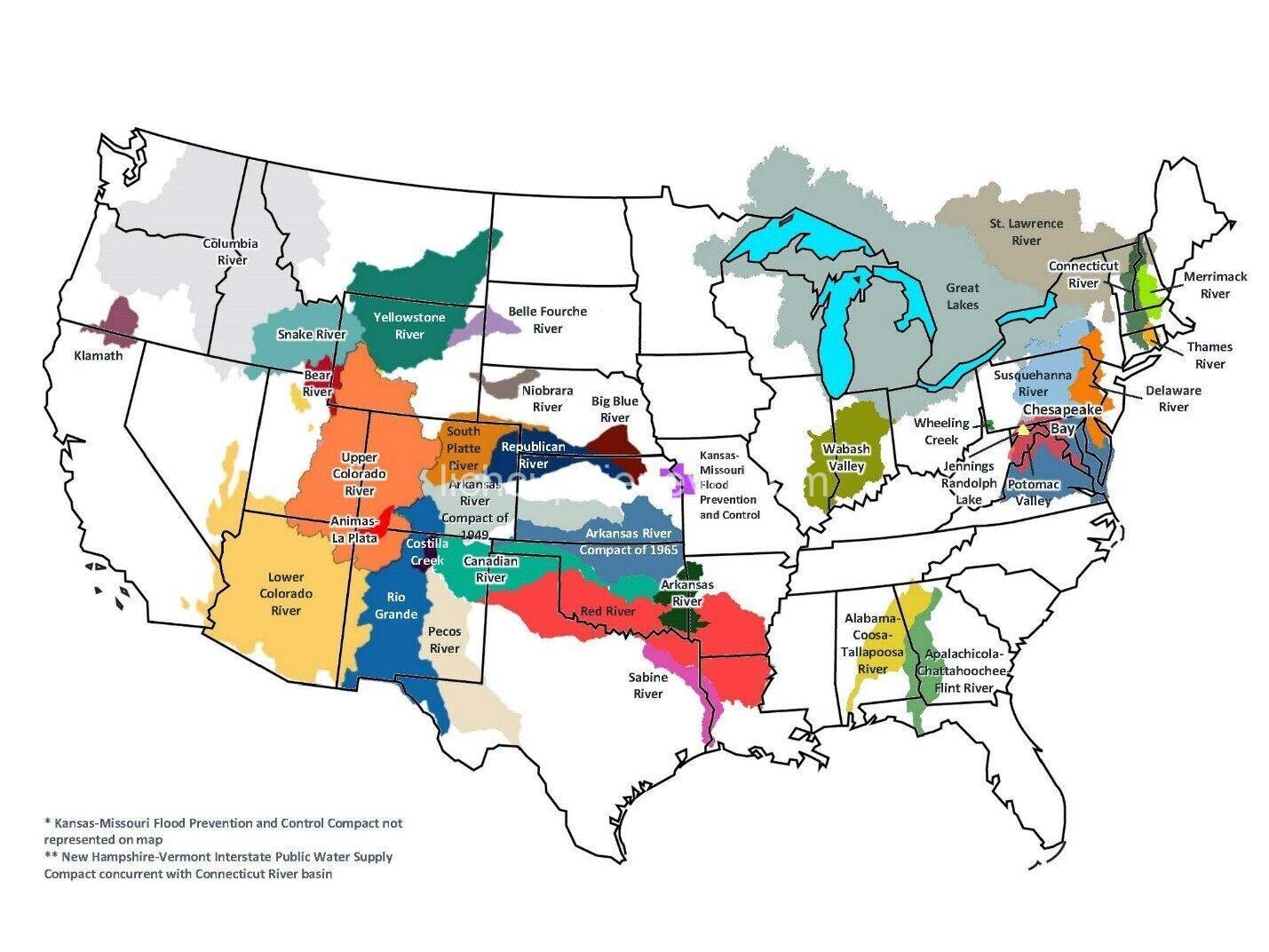
Examining the Consequences of Water Rights Conflicts Between States
Water rights conflicts have far-reaching consequences, impacting both the environment and society. Environmental degradation is a major concern, as water shortages and depletion threaten water sources. This scarcity can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity, putting delicate balances at risk. Furthermore, water pollution is a growing problem, as limited water resources become vulnerable to contamination from industrial discharge and agricultural runoff.
On the socioeconomic front, water rights conflicts can lead to agricultural losses and economic hardship, as farmers struggle to access sufficient water for irrigation. This can translate into higher water prices and affordability issues for consumers. Furthermore, tensions between states and communities can escalate, leading to social unrest and political instability.
Exploring Solutions and Strategies for Resolving Water Rights Conflicts
Finding sustainable solutions to interstate water disputes is crucial. Negotiation and cooperation are essential tools for resolving conflicts. Interstate compacts and agreements, along with collaborative water management programs, provide a framework for shared decision-making. Mediation and conflict resolution techniques can help facilitate dialogue and find common ground.
Water conservation and efficiency are critical for mitigating water scarcity. Implementing water-saving technologies and practices, promoting water conservation awareness, and adopting water-efficient landscaping and urban design can significantly reduce water demand.
Equitable distribution and allocation are vital for ensuring fairness and sustainability. Establishing water rights frameworks based on these principles, balancing the needs of different water users, and utilizing water markets and trading mechanisms can help promote responsible water management.
The federal government plays a crucial role in resolving interstate water disputes. Enforcing interstate compacts, providing funding and technical assistance, and promoting inter-agency coordination are essential functions in this context.
Case Studies of Interstate Water Conflicts
Several case studies highlight the challenges of managing interstate water resources. The Colorado River Basin, for instance, is home to numerous states with competing demands for water. The impact of water scarcity and over-allocation has been significant, requiring careful management and negotiation to balance needs and protect the river’s ecosystem.
The Appalachian Mountains present a different set of challenges. Competing interests and regional development pressures can create conflicts over water resources. Collaborative water management approaches are crucial for balancing needs and promoting sustainability.
The Mississippi River Basin represents a vast and complex ecosystem involving multiple states and diverse water users. Interstate compacts and regional collaboration are essential for managing water resources effectively and addressing potential conflicts.
The Future of Water Rights Management in a Changing World
Climate change is undeniably altering water availability and demand patterns. Adapting to these changes requires innovative solutions, such as water conservation, drought-resistant crops, and efficient irrigation systems. We also need to invest in mitigation strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
Technological advancements are paving the way for innovative water management solutions. Water desalination, water recycling, and smart water grids are emerging technologies with the potential to enhance water security and reduce our dependence on limited resources.
Public engagement is essential for building support for sustainable water management practices. Raising awareness, promoting community involvement, and encouraging stakeholder collaboration are crucial steps towards effective water management.
FAQs
What are the main challenges associated with interstate water conflicts?
Interstate water conflicts present several challenges, including:
- Scarcity and over-allocation: Limited water resources are often over-allocated to meet the needs of different states, leading to shortages and conflicts.
- Competing interests: States often have different priorities for water use, such as agriculture, industry, and urban development, creating tension over allocation.
- Lack of clear agreements: Ambiguous or incomplete interstate compacts can lead to disputes over the interpretation and enforcement of water rights.
- Political and economic factors: Political pressures and economic interests can influence water allocation decisions, sometimes at the expense of environmental sustainability.
What are the potential consequences of interstate water conflicts?
Interstate water conflicts can have significant environmental, socioeconomic, and political consequences, including:
- Environmental degradation: Water shortages and depletion can damage ecosystems, reduce biodiversity, and increase pollution.
- Economic hardship: Water scarcity can impact agricultural productivity, leading to higher water prices and economic losses for businesses.
- Social tensions: Conflicts over water can create divisions between states and communities, potentially leading to social unrest.
- Political instability: Interstate water disputes can exacerbate political tensions and contribute to instability in a region.
What are some solutions to interstate water conflicts?
Several solutions can help address interstate water conflicts, including:
- Negotiation and cooperation: Interstate compacts, collaborative water management programs, and mediation can facilitate cooperation and agreement among states.
- Water conservation and efficiency: Implementing water-saving technologies, promoting public awareness of conservation, and adopting water-efficient landscaping and urban design can reduce demand.
- Equitable distribution and allocation: Establishing fair and sustainable water rights frameworks, balancing the needs of different water users, and utilizing water markets can promote responsible water management.
- Role of the federal government: The federal government can play a crucial role by enforcing interstate compacts, providing funding and technical assistance, and promoting inter-agency coordination.
What are the key principles for managing interstate water resources effectively?
Effective management of interstate water resources requires adhering to several key principles:
- Sustainability: Water management practices must ensure the long-term health and availability of water resources.
- Equity: Water allocation should be fair and equitable, ensuring access to water for all users.
- Collaboration: States and communities need to work together to manage water resources effectively.
- Adaptation: Water management plans must be adaptable to changing conditions, including climate change and population growth.
What are some emerging trends in water rights management?
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of water rights management, including:
- Climate change adaptation: Water management strategies must address the challenges posed by climate change, such as drought and water scarcity.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in water desalination, water recycling, and smart water grids are providing new solutions for managing water resources.
- Public engagement: Increased public awareness and participation in water management decisions are essential for building support for sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Interstate water conflicts are a complex and multifaceted issue, demanding thoughtful solutions and a commitment to cooperation. By understanding the causes and consequences of these conflicts, we can work together to ensure the sustainable management of our precious water resources.
For more information and resources on water rights, electricity, and plumbing, visit Lichcupdienevn.com [http://lichcupdienevn.com/]. Share your thoughts and experiences with water rights conflicts in the comments below!
