Water Quality Monitoring Systems in Industrial Zones – Importance, Benefits & Challenges. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Water Quality Monitoring Systems in Industrial Zones
Water quality monitoring systems play a crucial role in safeguarding our environment and public health, especially in industrial zones where the potential for pollution is high. These systems are essential for detecting and preventing water contamination, ensuring compliance with regulations, and protecting our precious water resources. Let’s explore the key aspects of these systems.
Why is Water Quality Monitoring Important in Industrial Zones?
Industrial zones are often associated with various sources of pollution, including wastewater discharge, air emissions, and solid waste generation. These pollutants can significantly impact water quality, leading to various environmental and health problems.
- Environmental Impact of Industrial Pollution: Industrial pollution can contaminate water bodies, damaging aquatic ecosystems and impacting biodiversity. This includes the contamination of drinking water sources, harming human health and ecosystems.
- Public Health Risks Associated with Contaminated Water: Exposure to polluted water from industrial zones can pose serious health risks, leading to a range of illnesses, including waterborne diseases and chronic health conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance Requirements: Stringent regulations are in place to ensure the responsible management of industrial wastewater and prevent environmental pollution. Water quality monitoring systems are crucial for industries to comply with these regulations and avoid penalties.
Key Water Quality Parameters Monitored in Industrial Zones:
Water quality monitoring systems typically measure a range of parameters to assess the overall health of water bodies and identify potential pollution sources. These parameters fall into three main categories:
- Physical Parameters: These parameters reflect the physical characteristics of water and include temperature, pH, conductivity, and turbidity.
- Entity: Physical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Temperature
- Entity: Physical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: pH
- Entity: Physical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Conductivity
- Entity: Physical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Turbidity
- Chemical Parameters: These parameters measure the presence of specific chemicals in water, including dissolved oxygen, nutrients, heavy metals, organic compounds, and pesticides.
- Entity: Chemical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Dissolved Oxygen
- Entity: Chemical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Nutrients
- Entity: Chemical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Heavy Metals
- Entity: Chemical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Organic Compounds
- Entity: Chemical Parameter | Attribute: Category | Value: Pesticides
- Biological Parameters: These parameters assess the presence and abundance of living organisms in water, providing insights into the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem. This includes monitoring specific species and measuring the abundance of algae.
Types of Water Quality Monitoring Systems:
Different types of water quality monitoring systems are used to collect and analyze data, each with its own advantages and limitations.
- In-situ Monitoring: This involves deploying sensors directly in the water source, providing real-time data on water quality parameters.
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Type | Value: In-situ
- Laboratory Analysis: This involves collecting water samples and analyzing them in a laboratory for specific pollutants, offering high accuracy.
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Type | Value: Laboratory
- Remote Monitoring: This involves transmitting data from sensors wirelessly to a central control system, offering accessibility and real-time data visualization.
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Type | Value: Remote
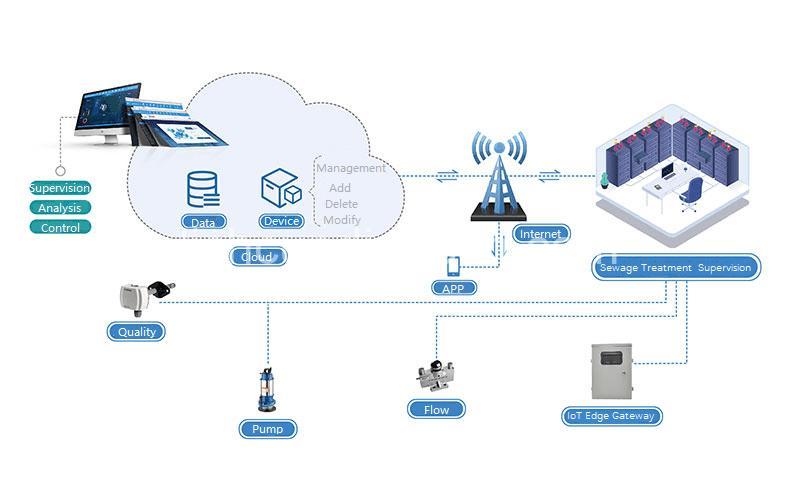
Benefits of Water Quality Monitoring Systems in Industrial Zones
The implementation of water quality monitoring systems in industrial zones brings significant benefits, contributing to environmental protection, public health safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Environmental Protection:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Improves | Entity: Environmental Protection
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Enables | Entity: Real-time Detection of Pollution Events
- Real-time detection of pollution events allows for prompt response and mitigation efforts, preventing further damage to water bodies and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Public Health Protection:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Promotes | Entity: Public Health Protection
- Monitoring systems ensure the safety of drinking water sources and protect public health by detecting and preventing contamination.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Facilitates | Entity: Regulatory Compliance
- These systems help industries comply with environmental regulations and meet legal requirements for water quality standards.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Water Quality Monitoring Systems
While water quality monitoring systems offer significant benefits, there are challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for their effective implementation.
- Cost and Installation:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Cost | Value: High
- The initial cost of installing and maintaining monitoring systems can be substantial, including equipment, sensors, data analysis software, and ongoing maintenance.
- Data Management and Interpretation:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Generates | Entity: Data
- Managing and interpreting large volumes of data generated by monitoring systems requires skilled personnel and advanced software tools.
- Security and Reliability:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Security | Value: Important
- Ensuring data security and reliability is critical, especially in remote monitoring systems. Robust security protocols are essential to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
Advancements in Technology for Water Quality Monitoring
Technological advancements are constantly improving the capabilities of water quality monitoring systems, making them more accurate, efficient, and cost-effective.
- Emerging Technologies for Enhanced Monitoring:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Technology | Value: Advanced Sensors
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Technology | Value: Data Analytics
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Technology | Value: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Advanced sensors, data analytics, and AI applications are transforming water quality monitoring, enabling more accurate and timely data collection and interpretation.
- Integrated Monitoring Systems:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Integration | Value: Multiple Data Sources
- Integrated monitoring systems combine data from multiple sources, such as water, air, and soil, providing a comprehensive understanding of environmental conditions.
Implementing and Promoting Water Quality Monitoring Systems
The successful implementation of water quality monitoring systems requires a collaborative approach involving industries, government agencies, and communities.
- Public Engagement and Awareness:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Relation: Requires | Entity: Public Engagement
- Public engagement and awareness are essential for promoting the adoption and effective use of these systems.
- Best Practices for Implementing Water Quality Monitoring Systems:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Implementation | Value: Best Practices
- Choosing the right monitoring system for specific needs, establishing clear goals and objectives, ensuring effective data collection and analysis, and communicating results to stakeholders are crucial for success.
Case Studies and Examples of Successful Water Quality Monitoring Systems
Numerous examples demonstrate the effectiveness of water quality monitoring systems in improving water quality and environmental protection.
- Highlight Real-world Applications of Water Quality Monitoring Systems:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Application | Value: Real-world Examples
- Case studies showcase how these systems have been successfully implemented in industrial zones, leading to significant improvements in water quality and environmental protection.
Future Directions for Water Quality Monitoring in Industrial Zones
The future of water quality monitoring in industrial zones holds exciting possibilities with continued advancements in technology and collaborative efforts.
- Continued Development of Advanced Technologies:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Future | Value: Advanced Technologies
- Ongoing research and development are expected to produce even more advanced sensors, data analytics, and AI applications, further enhancing monitoring capabilities and data interpretation.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing:
- Entity: Water Quality Monitoring System | Attribute: Future | Value: Collaboration
- Continued collaboration and knowledge sharing among industry, government, and research institutions will accelerate the adoption of best practices and promote the development of innovative solutions for water quality monitoring.
FAQs About Water Quality Monitoring Systems in Industrial Zones
Here are some frequently asked questions about water quality monitoring systems in industrial zones:
What are the most common pollutants found in industrial wastewater?
Industrial wastewater can contain a wide range of pollutants, depending on the specific industries involved. Some common pollutants include:
- Heavy Metals: Lead, mercury, cadmium, chromium
- Organic Compounds: Solvents, pesticides, pharmaceuticals
- Nutrients: Nitrogen and phosphorus
- Suspended Solids: Solids that do not dissolve in water, such as grit and sludge
How often should water quality be monitored in industrial zones?
The frequency of monitoring depends on various factors, including the type of industry, the potential for pollution, and regulatory requirements. However, monitoring should be conducted at least:
- Daily: For industries with high potential for pollution, continuous monitoring may be required.
- Weekly: For industries with moderate potential for pollution.
- Monthly: For industries with low potential for pollution.
What are the different types of sensors used in water quality monitoring systems?
Different types of sensors are used to measure various water quality parameters. Some common sensor types include:
- pH sensors: Measure acidity or alkalinity.
- Dissolved oxygen sensors: Measure the amount of oxygen dissolved in water.
- Conductivity sensors: Measure the ability of water to conduct electricity.
- Turbidity sensors: Measure the cloudiness or haziness of water.
How can industries ensure the accuracy and reliability of their water quality monitoring systems?
Industries should take several steps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their monitoring systems:
- Regular calibration of sensors: Ensure sensors are calibrated according to manufacturer specifications.
- Proper maintenance of equipment: Regularly maintain and repair equipment to ensure optimal performance.
- Data validation and verification: Implement procedures to validate and verify data collected by monitoring systems.
Conclusion
Water quality monitoring systems are crucial for protecting our environment, safeguarding public health, and ensuring compliance with regulations in industrial zones. By embracing these technologies, industries can contribute to a cleaner, healthier future. For more information about electrical and plumbing products and services, visit my website at http://lichcupdienevn.com. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
