Voltage Tester Guide: Types, Safety & How to Use It. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Voltage Testers: Types, Functions, and Safety
Before we delve into the specifics of using a voltage tester, let’s get a grasp on what voltage is and why it’s crucial to understand it.
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. Think of it as the force that pushes electrons through a wire. This force determines the strength of the electrical current.
Knowing the voltage in a circuit is important for several reasons. It helps us determine:
- Safety: A high voltage can be extremely dangerous. Using a voltage tester helps identify live wires, preventing accidental shocks.
- Troubleshooting: If an appliance or circuit isn’t working properly, a voltage tester can help determine if there’s a power supply problem or a fault within the device itself.
- DIY Projects: Understanding voltage is essential for anyone working on electrical projects. It allows you to ensure you’re working with the correct voltage for your components and to prevent safety hazards.
Now, let’s explore the different types of voltage testers available:
Non-Contact Voltage Tester (NCVT):
- How it works: An NCVT detects the presence of voltage by sensing the electromagnetic field generated by live wires. It doesn’t require direct contact with the wire.
- Advantages:
- Safety: Since it doesn’t touch the wire, it minimizes the risk of electrical shock.
- Easy to use: Simply point the NCVT towards the wire to detect voltage.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited accuracy: It can only indicate the presence or absence of voltage, not its exact value.
- Not effective with low voltage: NCVTs may not detect very low voltages.
- Common Applications: Preliminary checks, identifying live wires in outlets and appliances, quick troubleshooting.
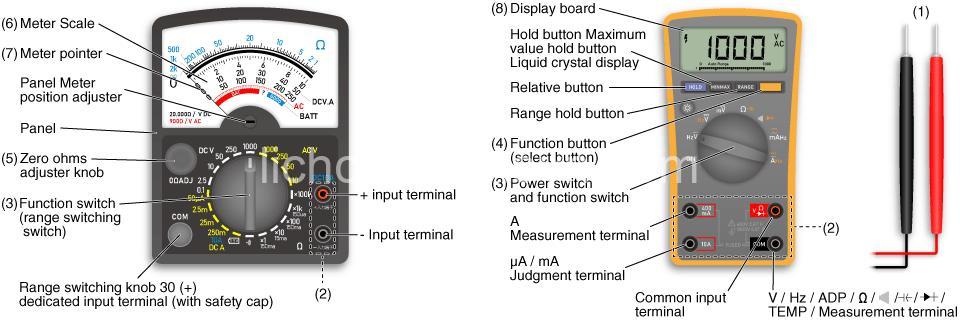
Contact Voltage Tester (Multimeter):
- How it works: A multimeter uses probes to make direct contact with the circuit and measures the voltage directly.
- Advantages:
- Accurate readings: It provides a precise measurement of voltage.
- Versatile: Multimeters can also measure other electrical properties like current and resistance.
- Disadvantages:
- Risk of electrical shock: Direct contact with live wires can be dangerous.
- More complex to use: Requires understanding how to set the multimeter correctly and interpret the readings.
- Common Applications: Detailed electrical measurements, troubleshooting complex electrical problems, advanced DIY projects.
Choosing the Right Voltage Tester:
- NCVT vs. Multimeter: The choice between an NCVT and a multimeter depends on your needs. If you’re mainly interested in quickly identifying live wires, an NCVT is sufficient. However, for more detailed measurements and troubleshooting, a multimeter is essential.
- Specific needs for different applications: Consider the types of electrical projects you plan to work on. If you’re working with low voltage circuits or require accurate readings, a multimeter is a better choice.
- Budget constraints: Voltage testers are available at various price points. Decide on a budget that suits your needs and the frequency of use.
Safety First: Precautions for Using a Voltage Tester
Using a voltage tester, whether an NCVT or a multimeter, requires a strong emphasis on safety. Remember, electricity can be dangerous, so it’s crucial to take precautions.
General Safety Practices:
- Always assume wires are live: Even if a circuit appears to be off, treat all wires as potentially carrying voltage.
- Never touch live wires with bare hands: Always use insulated tools or probes.
- Wear appropriate safety gear: Gloves and eye protection can help protect you from electrical shock and potential debris.
- Work in a well-lit area: Good lighting is essential for visibility and safety.
- Disconnect power source before working on electrical circuits: Always turn off the power at the breaker or fuse box before working on any wiring or electrical components.
Specific Safety Precautions for NCVTs:
- How to use an NCVT safely: Hold the NCVT by the insulated handle and point it towards the wire without touching it.
- Avoiding false readings: Keep the NCVT away from other electrical sources that may cause interference.
- Limitations of NCVTs: Remember that NCVTs only detect the presence of voltage, not its value. Don’t rely solely on an NCVT for precise measurements.
Specific Safety Precautions for Multimeters:
- Setting the multimeter to the correct voltage range: Ensure the multimeter is set to a range higher than the expected voltage to avoid damage to the meter and potential electrical shock.
- Connecting the probes correctly: Always connect the probes to the correct terminals on the multimeter, typically red for positive and black for negative.
- Avoiding electrical shock: Avoid direct contact with the probes while the multimeter is connected to a live circuit.
Using a Non-Contact Voltage Tester (NCVT) for Basic Checks
Once you’ve grasped the basics of using an NCVT safely, you can use it for simple checks.
- Identifying Live Wires: An NCVT typically uses a light or a beeping sound to indicate the presence of voltage. Hold the NCVT close to the wire you want to check. If the light illuminates or the beeper sounds, you’ve found a live wire.
- Identifying live wires in outlets, appliances, and wiring: You can use an NCVT to check for live wires in outlets, appliances, and wiring.
- Using NCVTs for preliminary checks before further testing: Before working on any electrical circuits, use an NCVT to quickly identify live wires, ensuring safety and preventing accidents.
Using a Contact Voltage Tester (Multimeter) for Detailed Measurements
Now, let’s move on to the multimeter. This tool is a powerful tool for precise electrical measurements and detailed troubleshooting.
-
Setting Up and Using a Multimeter:
- Selecting the appropriate voltage range: Before connecting the multimeter to a circuit, ensure it’s set to the correct voltage range. Choose a range slightly higher than the expected voltage.
- Connecting the probes to the multimeter correctly: Connect the red probe to the positive terminal on the multimeter and the black probe to the negative terminal.
- Measuring voltage in DC and AC circuits: Multimeters can measure both DC and AC voltage. The process is generally the same, but you’ll need to select the appropriate DC or AC setting on the multimeter.
-
Interpreting Multimeter Readings:
- Understanding voltage readings and their meaning: The multimeter will display the voltage in volts (V). Make sure you understand the unit of measurement and what the reading represents.
- Troubleshooting incorrect readings: If you’re getting an incorrect reading, check the multimeter settings, probe connections, and the circuit itself for any faults.
- Ensuring accurate measurements: For precise measurements, ensure the multimeter is calibrated and free from interference from other electrical sources.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful use, you might encounter issues with your voltage tester. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
-
The Voltage Tester is Not Working:
- Check the batteries: Make sure the batteries are fresh and properly installed.
- Ensure the probes are connected properly: Ensure the probes are securely connected to the multimeter.
- Verify the tester is in the correct mode: Double-check that the multimeter is set to the correct voltage mode (DC or AC).
- Inspect the tester for damage: Examine the tester for any visible damage, such as cracks or broken wires.
-
The Voltage Tester is Giving an Incorrect Reading:
- Make sure the tester is calibrated: Ensure the multimeter has been recently calibrated for accurate measurements.
- Avoid interference from other electrical sources: Keep the tester away from sources of interference, such as motors or electronic devices.
- Check for faulty wiring or loose connections: Inspect the wiring and connections in the circuit you’re testing for any loose or damaged wires.
Additional Applications of Voltage Testers
Beyond the basics, voltage testers have a wide range of applications:
-
Troubleshooting Electrical Appliances:
- Using a voltage tester to identify malfunctioning appliances: A voltage tester can help determine if an appliance is receiving power. If the appliance is not receiving power, it suggests a problem with the power supply or the appliance’s wiring.
- Checking for power supply issues: If an appliance is not working, a voltage tester can be used to verify that the power supply is functioning correctly.
- Diagnosing electrical problems in common appliances: A voltage tester can be used to check the voltage at different points within the appliance to pinpoint the location of the problem.
-
Testing Electrical Circuits:
- Using a voltage tester to check for continuity in circuits: A multimeter can be used to check for continuity in a circuit, ensuring there are no breaks or shorts.
- Identifying shorts or breaks in wiring: A multimeter can help identify short circuits or broken wires in a circuit.
- Testing the functionality of electrical components: A voltage tester can be used to check the voltage across individual components, such as switches, outlets, and wiring, to determine if they are functioning correctly.
Resources for Further Learning
If you’re interested in diving deeper into the world of voltage testers, I recommend checking out these resources:
-
Online Tutorials and Resources:
-
Professional Electrician Services:
- When to consult a professional for complex electrical work: If you’re unsure about a particular electrical project or dealing with complex circuits, it’s always wise to seek help from a qualified electrician.
- Finding reputable electricians in your area: Link to your website or your local directory of qualified electricians.
-
Safety Codes and Regulations:
- Understanding relevant electrical codes and regulations: Always refer to local electrical codes and regulations for safe electrical practices.
- Resources for learning more about safe electrical practices: Link to a resource for learning about safe electrical practices
FAQs About Voltage Testers
What are the risks of using a voltage tester incorrectly?
Using a voltage tester incorrectly can lead to serious electrical hazards. These include:
- Electrical Shock: Incorrectly using a contact tester can result in direct contact with live wires, leading to electrical shock.
- Damage to the Tester: Using a multimeter on the wrong setting or exceeding its voltage range can damage the tester.
- Fire Hazards: Faulty wiring or improper connections can result in electrical fires.
How often should I calibrate my multimeter?
It’s essential to regularly calibrate your multimeter to ensure accurate readings. As a general rule, multimeters should be calibrated at least once a year, or more frequently if they are used heavily or in harsh environments.
What is the difference between AC voltage and DC voltage?
- AC (Alternating Current) voltage: The voltage changes polarity continuously, flowing back and forth in a sinusoidal wave pattern. AC is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
- DC (Direct Current) voltage: The voltage flows in one direction only. DC power is used in devices like batteries and electronic circuits.
What are some common applications for voltage testers in DIY projects?
Voltage testers are useful for a variety of DIY projects, including:
- Troubleshooting electrical problems: Identifying broken wires, faulty outlets, or malfunctioning appliances.
- Checking voltage before working on circuits: Ensuring that the circuit is de-energized before working on it.
- Testing the functionality of electrical components: Checking if switches, outlets, and other components are working correctly.
Can I use a voltage tester to measure current?
While some multimeters can also measure current, a dedicated ammeter is typically recommended for measuring current. Voltage testers are primarily designed for measuring voltage, not current.
Conclusion
Using a voltage tester safely and effectively is crucial for anyone working with electricity. Remember, always prioritize safety and use the right tool for the job.
If you’re looking for high-quality electrical and plumbing products, visit link to your website. I’m always here to help, so feel free to leave any questions in the comments below. Share this article with your friends and family to spread the knowledge about electrical safety! And be sure to check out my website for more informative content on electricity and plumbing.
