Energy-Efficient Buildings & Government Regulations: A Guide. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
How Government Regulations Drive Energy Efficiency in Buildings
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of energy-efficient buildings in tackling climate change, reducing energy consumption, and improving public health. They have implemented various regulations to promote sustainable building practices and ensure that new and existing buildings meet specific energy performance standards. The driving forces behind these regulations are multifaceted:
- Environmental Concerns: Buildings contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, a major driver of climate change. Regulations aim to reduce this impact by mandating energy-efficient design, construction, and operation.
- Economic Benefits: Energy-efficient buildings save money on operating costs, reducing energy bills for building owners and tenants. This economic advantage makes energy-efficient upgrades more attractive for both residential and commercial properties.
- Resource Conservation: By minimizing energy consumption, regulations help conserve valuable natural resources, such as fossil fuels and water.
- Public Health: Energy-efficient buildings often promote better indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and overall health. This is because they reduce energy consumption, improve ventilation, and create more comfortable living and working environments.
The impact of government regulations on energy-efficient buildings is undeniable. Cities and countries that have implemented robust regulations have witnessed significant reductions in energy consumption, lower carbon footprints, and improved environmental performance. For instance, California’s building codes have led to substantial energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
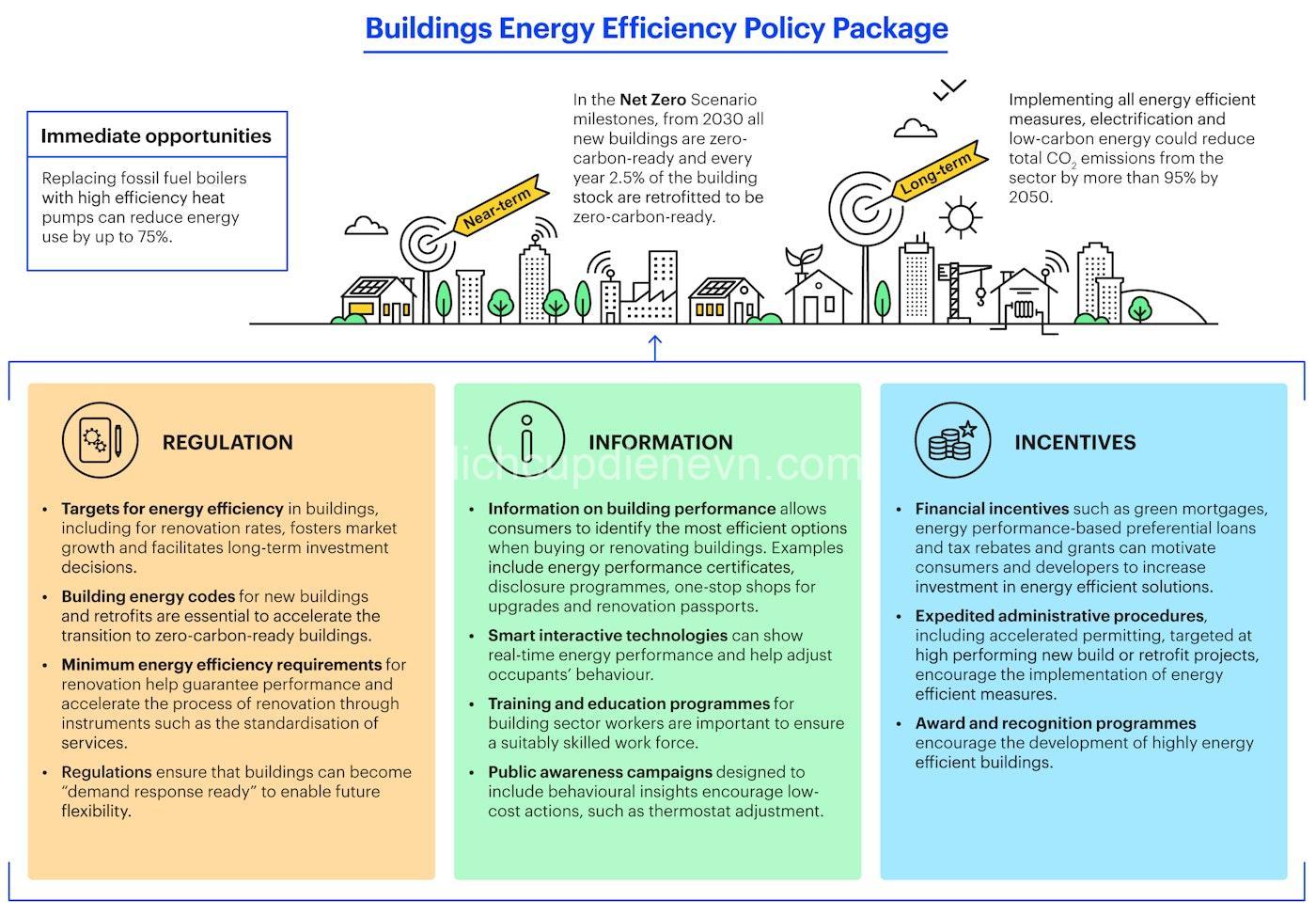
Types of Government Regulations for Energy-Efficient Buildings
Government regulations take various forms to promote energy-efficient buildings. These regulations act as a framework to guide the design, construction, and operation of buildings that use less energy and minimize their environmental impact. Here are some common types of regulations:
Building Codes:
Building codes establish minimum standards for the construction of buildings, ensuring safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency. They mandate specific requirements for things like insulation levels, window performance, and heating and cooling systems. For example, building codes often require a certain level of insulation for walls and roofs, specifying the minimum efficiency of windows, and dictating the use of energy-efficient appliances.
Energy Efficiency Standards:
Energy efficiency standards focus on the performance of individual building components, such as appliances, windows, and insulation. These standards ensure that building materials meet specific energy performance criteria. For example, an energy efficiency standard for refrigerators might set a minimum energy efficiency rating, while standards for windows might specify their heat-loss and heat-gain performance.
Incentives and Rebates:
To encourage homeowners and businesses to invest in energy-efficient upgrades, many governments offer financial incentives like tax credits, rebates, and grants. These incentives can reduce the upfront cost of implementing energy-saving measures, making them more attractive to building owners. For example, a homeowner might receive a tax credit for installing solar panels or a rebate for replacing old windows with energy-efficient ones.
Other Regulations:
In addition to building codes, energy efficiency standards, and incentives, other regulations can impact energy-efficient buildings, such as:
- Zoning Regulations: Zoning regulations control the use and development of land, including the design and construction of buildings. They can promote energy-efficient buildings by encouraging compact development, reducing reliance on cars, and promoting walkable neighborhoods.
- Building Permits: Building permits are required before construction can begin, and they often involve energy efficiency requirements. Building permit applications may require energy audits or the submission of plans that demonstrate compliance with energy efficiency standards.
The Impact of Government Regulations on Building Performance
Government regulations have a direct and measurable impact on building performance, leading to significant improvements in energy consumption, environmental performance, and public health.
Reduced Energy Consumption:
Regulations have been instrumental in reducing energy consumption in buildings. By mandating energy-efficient design, construction, and operation, these regulations have led to measurable energy savings. Studies have shown that buildings constructed after the implementation of energy efficiency standards consume significantly less energy than older buildings.
Improved Environmental Performance:
Energy-efficient buildings have a lower environmental impact, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet. Government regulations have been critical in reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with building energy consumption. By promoting the use of renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, these regulations are helping to mitigate climate change.
Enhanced Public Health:
Government regulations promote healthier and more comfortable indoor environments. Energy-efficient buildings often have better ventilation, improved thermal comfort, and reduced exposure to pollutants, contributing to a higher quality of life for occupants.
Challenges and Opportunities for Government Regulations
While government regulations have made significant progress in promoting energy-efficient buildings, several challenges remain. These challenges present opportunities for further improvements and innovation:
Implementation Challenges:
- Cost: Implementing energy-efficient building regulations can involve upfront costs for building owners and developers. Balancing the long-term cost savings of energy efficiency with the initial investment can be challenging.
- Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with building codes and energy efficiency standards can be difficult, especially for older buildings. Effective enforcement mechanisms are essential for achieving the intended energy-saving goals.
- Public Acceptance: Public acceptance of energy-efficient building regulations is crucial for their success. Education and awareness campaigns are needed to inform building owners and the general public about the benefits of these regulations.
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological innovation can make it challenging to keep up with the latest advancements in energy-efficient building technologies. Regulations should be flexible enough to adapt to new technologies and encourage innovation.
Future Directions:
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Government regulations are increasingly promoting the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into buildings. This trend will likely continue as technology improves and costs decrease.
- Stricter Regulations: As the urgency to address climate change intensifies, governments are likely to implement stricter regulations for energy-efficient buildings. These regulations may target higher performance standards, wider adoption of renewable energy, and improved building automation systems.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between governments, industry, and research institutions is crucial for driving innovation in the field of energy-efficient buildings. These partnerships can accelerate the development and deployment of new technologies and solutions.
Successful Case Studies of Government Regulations in Action
Many countries and cities have implemented successful government regulations for energy-efficient buildings, resulting in measurable improvements in energy consumption, environmental performance, and public health. Here are a few notable examples:
- California: California’s strict building codes and energy efficiency standards have led to significant reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations have made California a leader in promoting sustainable building practices.
- Germany: Germany’s energy efficiency regulations, particularly for new buildings, have been highly successful in reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions. The country’s “Passive House” standard sets very high energy performance standards for buildings.
- United Kingdom: The UK’s Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) are mandatory for all buildings, providing energy performance ratings that help buyers and renters make informed decisions. This system has increased awareness of energy efficiency and encouraged improvements in building performance.
The Future of Government Regulations for Energy-Efficient Buildings
Government regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy-efficient buildings. As concerns about climate change intensify, and technology continues to advance, these regulations are expected to become even more stringent and comprehensive.
- Integration of Smart Technologies: Governments are likely to encourage the integration of smart technologies, such as building automation systems and smart grids, to optimize energy consumption and improve building performance.
- Focus on Existing Buildings: Regulations may be expanded to cover existing buildings, promoting retrofits and upgrades to improve energy efficiency in older structures.
- Collaboration and Innovation: Continued collaboration between governments, industry, and research institutions will be essential to drive innovation and ensure the ongoing success of energy-efficient building regulations.
FAQs about Government Regulations on Energy-Efficient Buildings
What are the benefits of government regulations for energy-efficient buildings?
Government regulations for energy-efficient buildings offer a range of benefits, including:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Regulations help reduce energy consumption in buildings, resulting in lower energy bills for owners and tenants.
- Environmental Protection: Regulations contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Resource Conservation: They encourage the conservation of valuable natural resources, such as fossil fuels and water.
- Improved Public Health: Regulations promote better indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and overall health for building occupants.
How are government regulations enforced?
Enforcement mechanisms vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific regulation. Some common enforcement methods include:
- Building Inspections: Building inspectors check construction projects for compliance with building codes and energy efficiency standards.
- Penalties: Violators of regulations may face fines, penalties, or other legal actions.
- Certification Programs: Some regulations involve certification programs, where buildings are assessed for energy efficiency and awarded certifications, such as LEED or Energy Star.
What are the common challenges associated with implementing energy-efficient building regulations?
Implementing effective energy-efficient building regulations presents a number of challenges, including:
- Cost: The upfront costs of implementing energy-efficient measures can be a significant barrier for building owners.
- Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with regulations can be difficult, especially for existing buildings.
- Public Acceptance: Obtaining public acceptance of energy-efficient regulations can be challenging, requiring education and awareness campaigns.
- Technological Advancements: Keeping up with rapid advancements in energy-efficient building technologies can be difficult.
What are some examples of successful government regulations for energy-efficient buildings?
Several countries and cities have implemented successful regulations, including:
- California: California’s strict building codes and energy efficiency standards have led to significant energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Germany: Germany’s energy efficiency regulations have been highly effective in promoting energy-efficient buildings, with the “Passive House” standard setting a high bar for energy performance.
- United Kingdom: The UK’s Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) provide energy performance ratings for buildings, increasing awareness and promoting energy-efficient upgrades.
What is the future of government regulations for energy-efficient buildings?
Government regulations are expected to continue evolving to address emerging challenges and opportunities. Key areas for future focus include:
- Integration of Smart Technologies: Regulations will likely encourage the integration of smart technologies, such as building automation systems and smart grids, to optimize energy consumption.
- Focus on Existing Buildings: Regulations may be expanded to cover existing buildings, promoting retrofits and upgrades to improve energy efficiency in older structures.
- Collaboration and Innovation: Governments are expected to foster greater collaboration between industry, research institutions, and other stakeholders to drive innovation and ensure the ongoing success of energy-efficient building regulations.
Conclusion
Government regulations play a vital role in promoting energy-efficient buildings and achieving a more sustainable future. By setting energy performance standards, providing incentives, and enforcing compliance, these regulations drive innovation, reduce energy consumption, and protect the environment. To learn more about energy-efficient products and solutions for your home or business, visit lichcupdienevn.com. You can also contribute to the conversation by leaving comments, sharing this post, or exploring more content on our website!
