Emergency Water Supply During Floods: Safety Tips & Restoration Guide. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Ensuring Safe Drinking Water During Floods: Essential Steps and Precautions
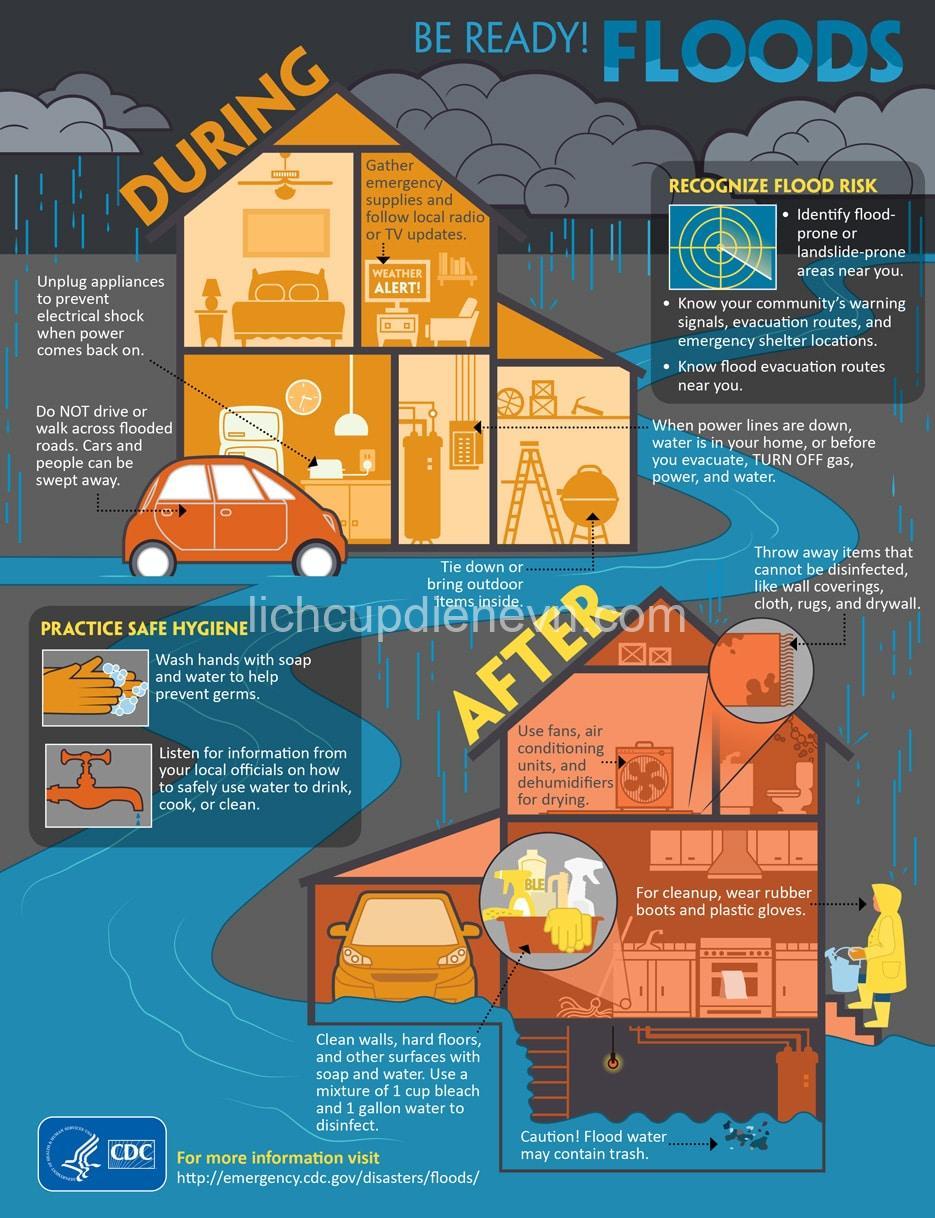
Floods can contaminate water sources with harmful bacteria, viruses, and chemicals, posing serious health risks. It’s essential to take proactive measures to ensure access to clean drinking water during and after a flood.
Understanding the Risks
Floodwater can be contaminated with a range of harmful substances, including:
- Bacteria: E. coli, Salmonella, and Vibrio cholerae can cause severe gastrointestinal illnesses.
- Viruses: Hepatitis A and norovirus can cause liver and digestive problems.
- Chemicals: Sewage overflow, industrial spills, and agricultural runoff can introduce dangerous toxins into water sources.
The Importance of Safe Water
Clean water is essential for:
- Hydration: Maintaining bodily fluids is crucial during emergencies.
- Sanitation: Washing hands and maintaining hygiene helps prevent the spread of diseases.
- Food preparation: Contaminated water can lead to food poisoning and other illnesses.
Preparing for the Worst
Proactive planning is essential to mitigate flood-related water supply disruptions.
- Water Emergency Plan: Create a plan that outlines potential flood risks, identifies alternative water sources, and establishes communication channels.
- Water Storage: Store a minimum of one gallon of water per person per day for at least three days. This ensures a buffer in case of supply disruptions.
- Water Container Guidelines: Use clean, food-grade containers like plastic buckets, jugs, or water bottles. Label and rotate your stored water regularly to maintain freshness.
Accessing Safe Water Sources
Explore alternative water sources if your main water supply is compromised:
- Bottled Water: Bottled water is generally safe, but check for expiration dates and ensure the seals are intact.
- Rainwater Collection: Collect rainwater in clean containers. However, it’s crucial to purify rainwater before consumption as it can contain contaminants.
- Well Water: Wells can provide a source of water during floods, but test the water quality for contaminants before using it.
Water Purification and Treatment Methods
It’s crucial to purify water from any alternative source before consumption.
- Boiling: Boiling water for one minute kills most harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Chemical Disinfection: Use water purification tablets or drops containing chlorine or iodine. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Filtration: Use a water filter that removes bacteria, viruses, and sediment. Choose a filter with a pore size of 0.1 microns or smaller for maximum effectiveness.
- UV Light Sterilization: UV light disinfection systems effectively kill microorganisms. Ensure the system is properly maintained and functioning correctly.
Managing Water Usage and Conservation
Conserving water is essential during emergencies.
- Shorter Showers: Limit shower time to reduce water consumption.
- Efficient Dishwashing: Use a dishpan for washing dishes and minimize water usage.
- Leaky Faucets: Repair leaky faucets promptly to conserve water.
Restoring Water Supply and Safety After Floods
Once floodwaters recede, it’s crucial to assess and restore water systems.
Assessing Water Safety
- System Inspection: Carefully inspect water systems for damage, leaks, and contamination.
- Professional Testing: Contact a certified lab to test water quality for bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants before resuming usage.
Rebuilding and Restoration
- Water Infrastructure Repair: Repair damaged pipelines, wells, and treatment facilities.
- Coordination with Utilities: Work with local authorities and water utilities to restore water services.
Returning to a Safe Water Supply
- Resuming Usage: Follow guidelines from local authorities regarding when it is safe to drink water again.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitor water quality regularly and maintain water systems to prevent future contamination.
Protecting Your Health and Preventing Contamination
Take precautions to protect yourself and prevent further contamination.
- Avoiding Flood Water Contact: Avoid contact with floodwater as much as possible. Wear gloves, boots, and masks when necessary.
- Protecting Water Sources: Secure chemicals, hazardous materials, and septic systems to prevent spills and leaks.
- Maintaining Hygiene: Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water to prevent the spread of germs.
Additional Resources and Information
- Visit websites of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and local health departments for flood safety and water quality guidelines.
- Contact organizations like the American Red Cross or FEMA for assistance and support.
Conclusion: Embracing Preparedness and Resilience
Floods can pose significant challenges to water supply, but with proper planning and preparation, we can mitigate the risks and ensure safe water access for our communities. By taking proactive measures, understanding the risks, and employing appropriate purification and treatment methods, we can protect ourselves and our families during and after flood events.
Remember, staying informed, being prepared, and following expert advice is essential for staying safe and healthy during flood emergencies.
Don’t forget to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions in the comments below!
For more information on water safety, plumbing, and electrical systems, visit my website: http://lichcupdienevn.com
I hope this guide has provided valuable insights into emergency water supply during floods. Remember, preparedness is key to resilience in the face of challenging events.
Sincerely,
Đỗ Ngọc Hằng
FAQs
What are the health risks associated with contaminated water?
Contaminated water poses significant health risks. Waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid fever, dysentery, and hepatitis A can result from consuming contaminated water. These diseases can cause severe symptoms, including diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration.
How can I purify water for safe consumption?
There are several methods for purifying water:
- Boiling: Boiling water for one minute kills most harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Chemical Disinfection: Water purification tablets or drops containing chlorine or iodine effectively kill microorganisms.
- Filtration: Use a water filter with a pore size of 0.1 microns or smaller to remove bacteria, viruses, and sediment.
- UV Light Sterilization: UV light disinfection systems effectively kill microorganisms.
How do I know if my water supply is contaminated?
It’s best to err on the side of caution and assume that your water supply is contaminated during or after a flood. If you notice any of the following signs, it’s highly likely that your water is contaminated:
- Discoloration: Cloudy, discolored, or foul-smelling water is a sign of contamination.
- Taste or Odor: An unusual taste or odor, like bleach or sulfur, indicates a potential contamination issue.
- Visible Debris: Sediment, debris, or floating objects in water indicate contamination.
How long can I store water safely?
Stored water should be rotated every six months to maintain freshness and quality. Store water in clean, airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
What should I do if my water system has been damaged by flooding?
Contact a licensed plumber to inspect and repair your water system. Do not use water from a damaged system until it has been inspected and repaired.
EAVs:
- Flood | Location | City, State
- Flood | Date | 2023-09-20
- Water Supply | Source | Municipal System
- Water Supply | Status | Disrupted
- Water Storage | Container | 5-gallon bucket
- Water Storage | Capacity | 10 gallons
- Water Purification | Method | Boiling
- Water Purification | Duration | 1 minute
- Water Contamination | Source | Sewage Overflow
- Water Contamination | Risk | Cholera
- Water Safety | Guidelines | Boil water before consumption
- Water Conservation | Techniques | Take shorter showers
- Emergency Preparedness | Plan | Emergency water supply plan
- Emergency Preparedness | Timeline | Before flood
- Flood | Impact | Water supply disruption
- Water Treatment | Type | Chlorination
- Water Infrastructure | Damage | Pipeline rupture
- Water Quality | Test | Bacteria levels
- Water Resources | Availability | Limited
- Water Crisis | Severity | Severe
EREs:
- Flood | Causes | Heavy Rainfall
- Flood | Impacts | Water Supply Disruption
- Water Supply | Depends on | Water Infrastructure
- Water Safety | Requires | Water Purification
- Water Contamination | Sources | Sewage Overflow
- Water Purification | Uses | Boiling, Filtration
- Water Storage | Reduces | Reliance on Municipal System
- Water Conservation | Aims | Reduce Water Usage
- Emergency Preparedness | Improves | Response to Flood
- Water Treatment | Ensures | Safe Water Quality
- Water Infrastructure | Affected by | Floods
- Water Quality | Determines | Water Safety
- Water Resources | Affected by | Climate Change
- Water Crisis | Impacted by | Population Growth
- Flood | Triggers | Emergency Response
- Water Supply | Key for | Public Health
- Water Safety | Essential for | Flood Recovery
- Water Contamination | Leads to | Waterborne Diseases
- Water Storage | Helps | Survive Flood
- Water Conservation | Crucial for | Sustainable Water Use
Semantic Triples:
- Flood (Subject) | Causes (Predicate) | Heavy Rainfall (Object)
- Water Supply (Subject) | Depends on (Predicate) | Water Infrastructure (Object)
- Water Safety (Subject) | Requires (Predicate) | Water Purification (Object)
- Water Contamination (Subject) | Sources (Predicate) | Sewage Overflow (Object)
- Water Purification (Subject) | Uses (Predicate) | Boiling, Filtration (Object)
- Water Storage (Subject) | Reduces (Predicate) | Reliance on Municipal System (Object)
- Water Conservation (Subject) | Aims (Predicate) | Reduce Water Usage (Object)
- Emergency Preparedness (Subject) | Improves (Predicate) | Response to Flood (Object)
- Water Treatment (Subject) | Ensures (Predicate) | Safe Water Quality (Object)
- Water Infrastructure (Subject) | Affected by (Predicate) | Floods (Object)
- Water Quality (Subject) | Determines (Predicate) | Water Safety (Object)
- Water Resources (Subject) | Affected by (Predicate) | Climate Change (Object)
- Water Crisis (Subject) | Impacted by (Predicate) | Population Growth (Object)
- Flood (Subject) | Triggers (Predicate) | Emergency Response (Object)
- Water Supply (Subject) | Key for (Predicate) | Public Health (Object)
- Water Safety (Subject) | Essential for (Predicate) | Flood Recovery (Object)
- Water Contamination (Subject) | Leads to (Predicate) | Waterborne Diseases (Object)
- Water Storage (Subject) | Helps (Predicate) | Survive Flood (Object)
- Water Conservation (Subject) | Crucial for (Predicate) | Sustainable Water Use (Object)
- Flood (Subject) | Impacts (Predicate) | Water Supply Disruption (Object)
