Electricity Supply Challenges in Developing Regions: Bridging the Access Gap. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding the Electricity Access Gap in Developing Regions
Imagine a world where basic necessities like lighting, refrigeration, and communication are out of reach for millions of people. This is the harsh reality for a significant portion of the global population, particularly in developing regions. While urban areas often enjoy reliable electricity access, rural communities face a stark reality – energy poverty.
The lack of reliable and affordable electricity access has a profound impact on every aspect of life in developing regions. It hinders economic growth, limits educational opportunities, and undermines health and well-being.
The Scale of the Problem:
Consider these staggering statistics:
- Over 780 million people lack access to electricity globally, with the majority residing in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- The percentage of the population without access to electricity is significantly higher in rural areas compared to urban centers.
- The World Bank estimates that energy poverty costs developing countries billions of dollars annually in lost productivity and economic potential.
Causes of the Energy Access Gap:
The energy access gap is a complex problem with a multitude of contributing factors:
- Limited Infrastructure: The lack of robust power generation capacity, transmission lines, and distribution networks poses a significant barrier to electrification.
- Financial Constraints: Developing countries often face limited investment capital for energy infrastructure development. High energy costs also hinder access, making it difficult for low-income households to afford electricity.
- Technical Challenges: Aging infrastructure, limited technical expertise, and grid unreliability contribute to the problem.
The Impact of Limited Electricity Access:
The consequences of limited electricity access are far-reaching and impact every aspect of life:
- Economic Development: It hampers industrial growth, limits job creation, and restricts economic opportunities.
- Health and Well-Being: It impedes access to essential healthcare services, limits educational opportunities, and contributes to increased health risks.
- Social Inequality: It disproportionately impacts marginalized communities, women, and children, exacerbating existing social inequalities.
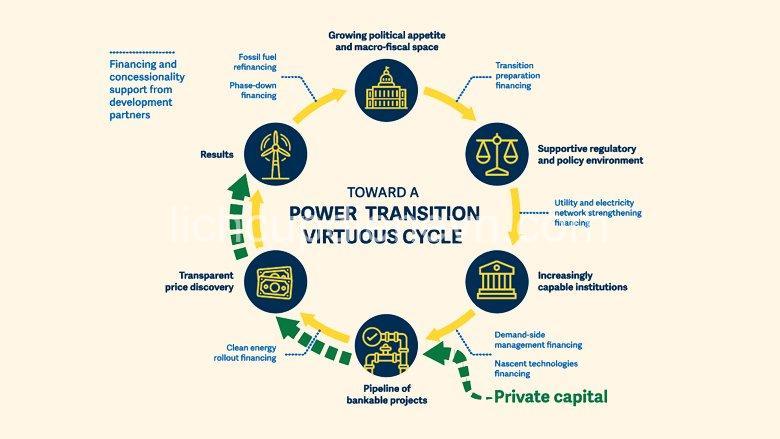
Exploring Solutions and Strategies for Sustainable Electrification
Addressing the energy access gap requires a comprehensive approach that tackles the underlying challenges and fosters sustainable electrification.
-
Investing in Infrastructure Development:
-
Expanding Generation Capacity: It is crucial to invest in both traditional and renewable energy sources to meet growing demand. This includes building new power plants, upgrading existing facilities, and leveraging the potential of solar, wind, and hydropower.
-
Strengthening Grid Infrastructure: Expanding and modernizing transmission and distribution networks are essential for delivering electricity to remote areas. This requires investments in grid infrastructure, smart grid technologies, and maintenance programs.
-
Addressing Financial Constraints:
-
Public-Private Partnerships: Attracting private sector investment is critical. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) offer a viable model, leveraging the expertise and resources of both public and private sectors.
- International Development Aid: Increased support from international development agencies and financial institutions is essential for funding energy projects, providing concessional financing, and facilitating technology transfer.
-
Microfinance: Microfinance can empower individuals and communities to invest in off-grid energy solutions, such as solar home systems.
-
Harnessing the Power of Renewable Energy:
-
Decentralized Energy Systems: Microgrids and off-grid solutions offer promising alternatives for reaching remote areas.
- Energy Storage Technologies: Advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, play a crucial role in addressing the intermittency issues associated with renewable energy sources.
-
Renewable Energy Policy: Strong policies and regulations are essential to incentivize renewable energy deployment, attract investments, and create a favorable environment for renewable energy businesses.
-
Promoting Energy Efficiency:
-
Energy Efficiency Technologies: Adopting energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting, high-efficiency appliances, and smart meters, can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Awareness and Training: Raising awareness about energy efficiency and providing training programs to promote responsible energy use are vital.
- Building Codes and Standards: Establishing building codes and standards that encourage energy efficiency in new construction and renovation projects can have a lasting impact.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Numerous initiatives around the world are demonstrating the effectiveness of different electrification approaches.
- Power Africa: The Power Africa initiative, launched in 2013, aims to double access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa. The initiative leverages public-private partnerships, promotes renewable energy development, and focuses on grid expansion and off-grid solutions.
- India’s Rural Electrification Programme: India’s ambitious rural electrification program has made significant progress in connecting rural areas to the grid, using a mix of traditional and renewable energy sources.
- The World Bank’s Energy Sector Support: The World Bank provides substantial financing and technical assistance to developing countries for energy sector development, supporting projects related to grid expansion, renewable energy deployment, and energy efficiency programs.
The Future of Electrification in Developing Regions
-
Emerging Trends and Innovations: Advancements in technology are revolutionizing the energy landscape.
- Mini-grids: Mini-grids are becoming increasingly popular, providing localized electricity solutions for small communities and off-grid areas.
- Energy Storage: Next-generation battery technologies and other energy storage options are making renewable energy more reliable and accessible.
- Decentralized Energy Markets: Blockchain technology is facilitating the development of peer-to-peer energy trading platforms, empowering communities to manage their energy resources.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are playing an increasingly significant role in optimizing grid management, enhancing grid resilience, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
-
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks:
-
Supportive Policy Environment: Governments play a vital role in creating conducive policy environments that encourage investment in sustainable energy. This includes providing tax incentives, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs for renewable energy projects.
- Regional Cooperation: Collaboration between countries can accelerate progress. This includes sharing best practices, coordinating infrastructure development, and facilitating cross-border energy trade.
Sustainable Electrification: A Global Imperative
- Global Development Goals: Achieving universal energy access is a critical component of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It is essential for reducing poverty, improving health, and fostering economic growth.
- The Role of Technology: Technology is a powerful tool for driving sustainable electrification.
- Global Collaboration: Achieving universal energy access requires a collective effort. This includes international cooperation, technology transfer, and knowledge sharing.
What are the main challenges in providing electricity in developing regions?
The main challenges in providing electricity in developing regions include:
- Lack of Infrastructure: Developing regions often lack adequate power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure to meet the growing demand for electricity.
- Financial Constraints: Limited investment capital, high energy costs, and lack of access to financing hinder infrastructure development and electrification efforts.
- Technical Expertise: A shortage of skilled personnel in the energy sector can hamper the effective operation and maintenance of power infrastructure.
- Social and Environmental Challenges: Ensuring equitable access to electricity, mitigating the environmental impact of energy generation, and balancing development needs with environmental concerns are crucial considerations.
How can renewable energy sources address electricity supply challenges?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution to electricity supply challenges in developing regions. Renewable energy technologies:
- Reduce reliance on fossil fuels: This mitigates carbon emissions and contributes to combating climate change.
- Provide a more reliable energy source: Solar and wind power can often be more reliable than traditional power sources in remote areas.
- Create local job opportunities: The development and maintenance of renewable energy projects can create employment opportunities in rural communities.
What are the potential benefits of smart grids in developing regions?
Smart grids offer numerous advantages for developing regions:
- Improved grid efficiency: Smart grids enhance energy efficiency by optimizing power distribution and reducing losses.
- Increased grid resilience: They enhance grid resilience by enabling real-time monitoring and control, reducing the impact of outages and disruptions.
- Integration of renewable energy: Smart grids facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, enabling a more sustainable energy mix.
How can public-private partnerships contribute to sustainable electrification?
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) offer a viable model for accelerating sustainable electrification in developing regions.
- Leveraging Private Sector Resources: PPPs attract private sector expertise, capital, and technology, which can be crucial for infrastructure development.
- Sharing Risk and Responsibility: PPPs share risks and responsibilities between public and private sectors, reducing the financial burden on governments.
- Promoting Innovation: PPPs can foster innovation and encourage the adoption of new technologies in the energy sector.
Conclusion
The challenge of providing reliable and affordable electricity access to developing regions is a global priority. By understanding the complexities of the energy access gap, embracing innovative solutions, and fostering global collaboration, we can work towards a future where everyone enjoys the benefits of sustainable and reliable energy.
For more information about electrical and plumbing products, you can visit my website at http://lichcupdienevn.com. Please share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below.
I hope this article has been helpful! Please share and subscribe for more information about electricity and water.
