Drought Impact on Regional Water Supply: Understanding Scarcity, Quality & Conflicts. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
How Drought Affects Regional Water Supply
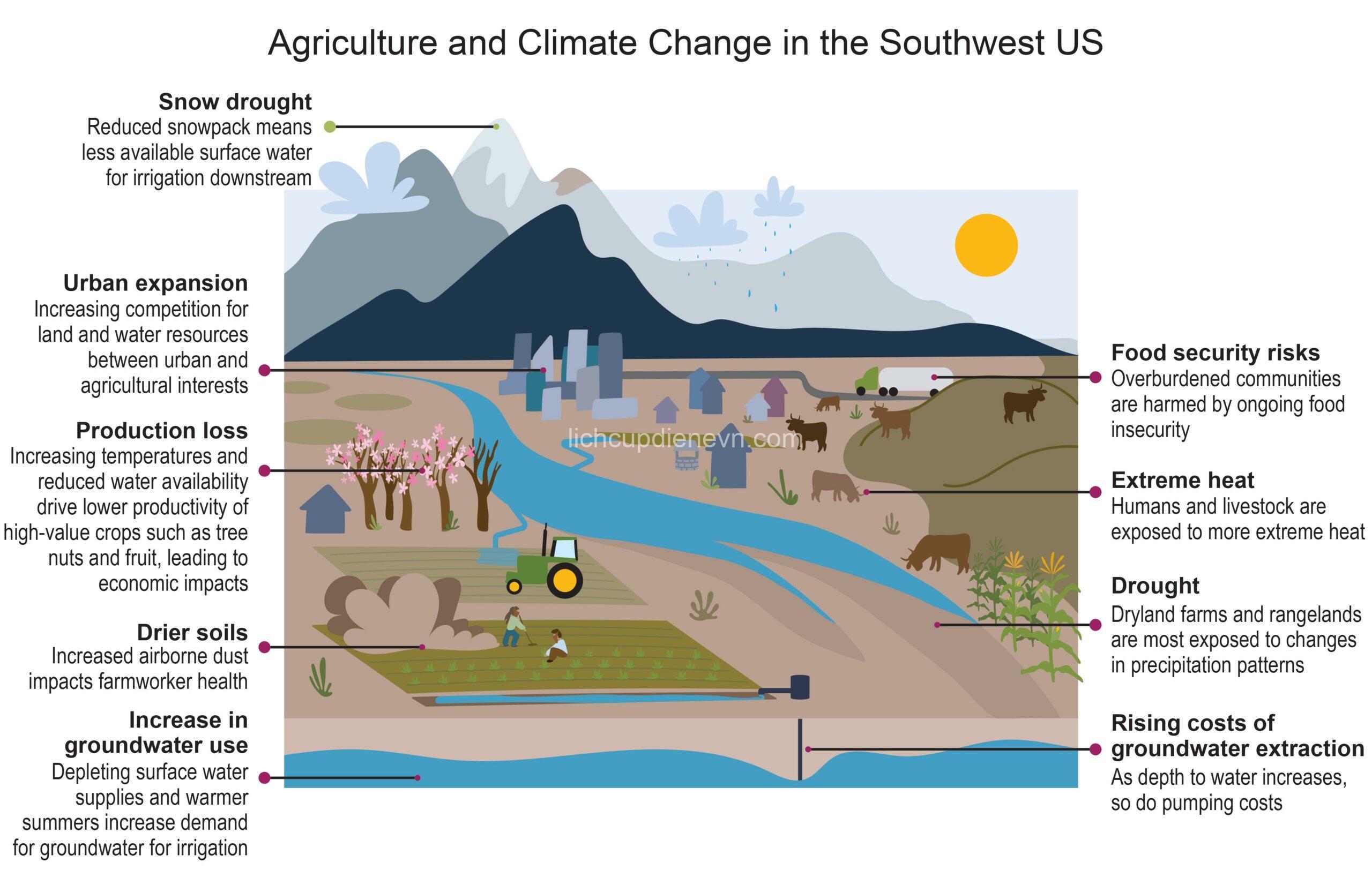
Drought, a prolonged period of below-average precipitation, significantly impacts the availability of water resources in different regions. The impact of drought on regional water supply is a pressing issue with far-reaching consequences for agriculture, industry, ecosystems, and society.
Imagine a river, usually brimming with water, shrinking to a mere trickle. That’s the stark reality of drought. As precipitation decreases, river flows dwindle, groundwater levels decline, and reservoir storage diminishes. This reduced water availability directly affects various sectors that rely on these sources.
Agriculture, the backbone of many economies, suffers significantly. Crop yields decline, livestock struggle to find water, and irrigation systems become less effective. Industry faces challenges as well. Production processes that rely on water become less efficient, leading to reduced output and higher costs. Even domestic water use, a necessity for daily life, is impacted. Water rationing and restrictions become commonplace, forcing communities to adjust their water consumption habits.
The Consequences of Drought on Water Quality
Drought not only reduces water availability but also deteriorates water quality. As water levels decline, evaporation intensifies, leading to increased salinity. This concentrated salt content can make water unsuitable for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
Reduced water flow also allows for the concentration of pollutants from agricultural runoff, sewage, and industrial waste. These contaminants can contaminate water sources and pose health risks. Furthermore, drought conditions can create environments favorable for harmful algal blooms, which can produce toxins detrimental to human health and ecosystems.
The consequences of degraded water quality are multifaceted. Human health is at risk due to the potential for waterborne diseases from consuming contaminated water. Ecosystems suffer as degraded water quality affects aquatic life, disrupting biodiversity and overall ecological balance.
Drought-Induced Water Stress and Conflicts
Drought intensifies competition for limited water resources, leading to water stress and conflicts. Regions dependent on shared water sources may find themselves embroiled in disputes over water allocation, leading to inter-regional conflicts.
Inter-sectoral conflicts arise as different sectors – agriculture, industry, and domestic use – compete for limited water resources. This competition can lead to tension and disagreements over water allocation and usage priorities.
Furthermore, social conflicts can arise within communities due to limited water resources, especially impacting marginalized groups who lack access to reliable water infrastructure and resources. The vulnerability of these communities is exacerbated by drought, leading to food insecurity, displacement, and social unrest.
The Economic Impact of Drought on Regional Water Supply
The economic consequences of drought-induced water scarcity are far-reaching. Agriculture, a major contributor to GDP in many regions, suffers significant economic losses. Reduced crop yields lead to lower farm income, impacting livelihoods and overall economic stability. Livestock losses further exacerbate these economic hardships.
Industry is also vulnerable. Water-intensive industries experience production disruptions and cost increases, leading to reduced output and potential job losses. The tourism sector, which relies on water-based recreational activities, suffers from reduced visitor numbers and closures, impacting local economies.
The Impact of Drought on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Drought profoundly impacts ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, plant and animal mortality, and altered biodiversity. Declining water levels, reduced water flow, and changes in water quality disrupt ecological processes and force species to adapt or face extinction.
Healthy ecosystems play a vital role in mitigating drought impacts and supporting water availability. Wetlands, forests, and riparian zones act as natural water retention areas, buffering against drought impacts by regulating water infiltration, groundwater recharge, and overall water cycle regulation. The loss of these ecosystems exacerbates drought effects and diminishes water resilience.
Strategies for Adaptation and Mitigation
Addressing drought challenges requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Water conservation plays a crucial role in reducing water demand. Implementing water-efficient appliances, water-saving gardening practices, and responsible water use habits are essential for households. Agriculture can adopt drought-tolerant crops, efficient irrigation systems, and water-harvesting techniques to minimize water consumption. Industry needs to embrace water-efficient processes, waste-water recycling, and responsible water management practices to reduce its water footprint.
Water-efficient technologies and practices play a vital role in optimizing water use and promoting sustainable water use. These technologies can help reduce water consumption, improve water management efficiency, and ensure the long-term availability of water resources.
Effective water management strategies are essential to manage drought impacts. Implementing water rationing, demand management, and pricing mechanisms can help regulate water usage and ensure equitable access to water resources during drought.
Drought Preparedness and Early Warning Systems
Developing drought preparedness plans and early warning systems is crucial for mitigating drought impacts and ensuring a coordinated response.
Meteorological data and hydrological models can be used for drought forecasting, providing early warning of potential drought conditions. This information allows for timely action to implement drought preparedness strategies and minimize the impacts of drought.
Community involvement in drought preparedness is essential. Public education, community engagement, and collaboration are key to developing and implementing effective drought preparedness strategies.
Addressing Climate Change for Drought Resilience
Addressing climate change is crucial to reducing drought frequency and severity. Climate change exacerbates drought conditions, highlighting the urgency of climate action.
Renewable energy sources and carbon emissions reduction are essential for mitigating climate change and reducing its impacts on drought. Transitioning to a low-carbon economy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions can help mitigate the effects of climate change and create a more resilient future.
Developing regional adaptation strategies is essential to cope with the impacts of drought. These strategies should be tailored to the unique conditions and vulnerabilities of different regions, taking into account factors such as climate, water infrastructure, and socioeconomic conditions.
Case Studies of Drought Impacts and Adaptation
Case studies from different regions around the world provide valuable insights into the impacts of drought and the effectiveness of adaptation strategies. Learning from these experiences can inform future drought management practices and promote global collaboration.
Lessons learned from these case studies highlight the importance of cross-sectoral cooperation, collaborative water management, and proactive drought preparedness. These approaches are critical for building drought resilience and ensuring sustainable water management.
Looking Ahead: Future Directions for Drought Management
Continued research and development of innovative solutions is crucial for managing drought challenges. Investing in scientific research, exploring new technologies, and developing innovative approaches are essential for addressing the complexities of drought.
Policy interventions, investment in infrastructure, and public awareness campaigns are vital for supporting drought management. Strong government policies, robust infrastructure development, and public education can foster sustainable water management practices and build drought resilience.
International collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for addressing global drought challenges. Sharing best practices, research findings, and technological innovations on a global scale can accelerate the development of effective drought solutions and build a more sustainable future.
What are the main causes of drought?
Drought is primarily caused by a lack of precipitation over an extended period, leading to a decline in water availability. However, several factors can contribute to drought, including:
- Climate Change: Global warming alters weather patterns, leading to increased evaporation and reduced precipitation, making droughts more frequent and severe.
- Deforestation: Removing forests reduces evapotranspiration, which contributes to the water cycle and can impact precipitation patterns.
- Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can lead to soil degradation and erosion, reducing water infiltration and increasing runoff.
- Poor Water Management: Inefficient irrigation practices, overuse of groundwater, and inadequate water infrastructure can exacerbate drought impacts.
What are the main impacts of drought on agriculture?
Drought significantly impacts agriculture, leading to:
- Reduced Crop Yields: Lack of water reduces crop growth and productivity, leading to lower yields and reduced income for farmers.
- Livestock Losses: Drought can lead to livestock deaths due to lack of water and forage, impacting food production and farmer livelihoods.
- Increased Irrigation Costs: Farmers may need to invest in more efficient irrigation systems or rely on expensive water sources, increasing costs and reducing profitability.
What are the main impacts of drought on ecosystems?
Drought can have devastating impacts on ecosystems, leading to:
- Habitat Loss: Declining water levels, reduced water flow, and changes in water quality can alter ecosystems and lead to habitat loss for various species.
- Plant and Animal Mortality: Drought can directly impact plants and animals, leading to increased mortality rates and changes in population dynamics.
- Altered Biodiversity: Drought can disrupt ecological processes and reduce biodiversity, leading to long-term consequences for ecosystem health and stability.
What are some solutions to mitigate drought impacts?
Mitigating drought impacts requires a comprehensive approach encompassing:
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-efficient technologies, promoting responsible water use habits, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Drought Preparedness: Developing drought preparedness plans, establishing early warning systems, and promoting community awareness and engagement.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in water infrastructure, such as dams, reservoirs, and water treatment plants, to enhance water security and resilience.
- Policy Interventions: Implementing policies that promote sustainable water management, incentivize water conservation, and support drought-affected communities.
Conclusion
Drought is a complex and challenging issue with profound impacts on regional water supply. Understanding how drought affects water availability, quality, and creates conflicts is crucial for developing effective solutions. By implementing water conservation measures, promoting drought preparedness, addressing climate change, and fostering international collaboration, we can build resilience to drought and ensure sustainable water management for future generations.
*Visit lichcupdienevn.com to learn more about electrical and plumbing products that can help conserve water and enhance your home’s water efficiency. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with drought in the comments below. *
Đỗ Ngọc Hằng
