Smart Meter Deployment: Benefits, Challenges & Future | Lichcupdienevn.com. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding the Benefits of Smart Meter Deployment
Smart meters are revolutionizing the way we consume energy, offering a range of benefits that extend beyond simple billing. They provide real-time data, enabling consumers to track their energy consumption and make informed decisions about their usage. This level of detail allows for more effective energy management, ultimately leading to significant savings and a reduction in environmental impact.
How Smart Meters Improve Energy Efficiency:
Imagine having a window into your energy usage, allowing you to see exactly how much electricity each appliance consumes in real-time. That’s the power of a smart meter! This level of detail allows you to identify areas of energy waste, such as appliances left on standby or inefficient lighting. Armed with this knowledge, you can make conscious choices to reduce your energy consumption, leading to lower energy bills and a lighter environmental footprint.
Smart meters also facilitate demand response programs, where utilities can adjust energy prices based on real-time demand. This encourages consumers to shift their energy usage away from peak hours, minimizing strain on the grid and reducing overall energy costs. By providing consumers with the tools to actively manage their energy consumption, smart meters empower them to take control of their energy usage and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Smart Meters and Enhanced Grid Management:
The data collected by smart meters provides valuable insights into energy demand patterns, allowing utilities to optimize grid operations and improve overall efficiency. This data-driven approach helps utilities forecast energy demand more accurately, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of electricity. Furthermore, smart meters enable utilities to integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, seamlessly into the grid. This helps to create a more diversified and sustainable energy system, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a cleaner environment.
By providing real-time data on energy demand, smart meters can help utilities identify and address potential grid bottlenecks. This proactive approach allows for better grid management, reducing the risk of blackouts and ensuring a reliable flow of electricity to consumers.
The Impact of Smart Meters on Customer Service:
Smart meters are transforming customer service in the energy sector, providing faster, more accurate, and convenient billing cycles. With real-time data, utilities can generate accurate bills based on actual energy consumption, minimizing errors and disputes.
Moreover, smart meters enable utilities to communicate with customers more effectively. Utilities can send alerts about potential energy savings, provide personalized recommendations, and offer tailored energy management tools, all based on individual customer data. This personalized approach improves customer satisfaction and empowers consumers to take greater control of their energy usage.
Smart meters also streamline remote meter reading and account management, eliminating the need for manual meter readings and allowing for faster and more efficient service. This technology empowers customers to manage their accounts online, access their energy consumption data, and receive real-time alerts, all from the comfort of their homes.
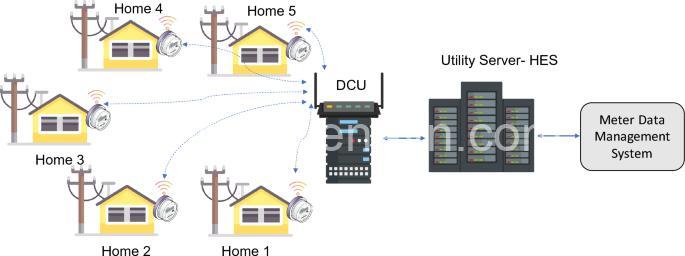
Exploring the Challenges of Smart Meter Deployment
While the benefits of smart meter deployment are undeniable, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. These include concerns about cost, privacy, and technical implementation.
Cost Considerations for Smart Meter Deployment:
The initial investment in smart meters can be significant, as it requires purchasing new meters, upgrading infrastructure, and training personnel. However, the long-term benefits, including reduced energy consumption and improved grid efficiency, can outweigh these initial costs.
Several funding models and incentives are available to support smart meter deployment. These include government subsidies, rebates, and tax credits, which can help offset the initial investment for utilities and consumers. Additionally, utilities can leverage data analytics to identify areas for cost optimization, reducing the overall cost of smart meter deployment.
Addressing Privacy Concerns Associated with Smart Meter Data:
One of the key concerns surrounding smart meter deployment is data privacy. Smart meters collect detailed information about energy consumption, raising questions about how this data is used, stored, and protected.
To address these concerns, robust data security measures and encryption protocols are implemented. This ensures that data is protected from unauthorized access and misuse. Regulatory frameworks are also in place to protect consumer data privacy, defining guidelines for data collection, storage, and access.
Transparency and control over personal energy consumption information are crucial for ensuring consumer trust. Utilities should provide clear information about data collection practices, allow consumers to access and manage their data, and offer options for data anonymization.
Technical Challenges and Solutions for Smart Meter Implementation:
Ensuring seamless integration of smart meters with existing infrastructure is a crucial technical challenge. This involves addressing interoperability issues between different meter types and communication networks. Additionally, ensuring reliable communication networks and data transfer is essential for accurate and timely data collection and analysis.
Cybersecurity threats pose a significant challenge, as smart meters are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity protocols are essential for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and manipulation. Implementing standardized protocols for seamless integration of smart meters with the grid and other systems is also crucial for efficient operation and interoperability.
Case Studies and Examples of Smart Meter Deployment
Successful Smart Meter Deployment Projects and Their Outcomes:
Numerous cities and states have successfully implemented smart meter programs, demonstrating the benefits of this technology. For example, the city of Austin, Texas, has seen a significant reduction in energy consumption and improved grid reliability since deploying smart meters. Similarly, the state of California has achieved significant progress in integrating renewable energy sources into the grid thanks to smart meter data.
These successful deployments highlight the positive impact of smart meters on energy efficiency, grid management, and customer satisfaction. They demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of this technology, providing valuable lessons for other regions looking to implement smart meter programs.
Lessons Learned from Smart Meter Deployment Challenges:
While many smart meter deployments have been successful, there have also been challenges. One common challenge is the lack of planning and stakeholder engagement. Failure to involve all stakeholders, including utilities, consumers, and policymakers, can lead to delays, resistance, and unforeseen difficulties.
Another challenge is the lack of standardization. Different meter types and communication networks can create interoperability issues, making it difficult to integrate smart meters with existing infrastructure.
From these experiences, it’s evident that successful smart meter deployment requires careful planning, effective communication, and a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders.
The Future of Smart Meter Deployment
Advancements in Smart Meter Technology and Applications:
The future of smart meter technology is exciting, with advancements in areas such as Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI). AMI allows for more sophisticated data collection and analysis, enabling utilities to manage the grid more effectively and provide enhanced customer service.
Smart meters are increasingly being integrated with smart home devices, creating interconnected ecosystems that can optimize energy usage and enhance comfort. AI algorithms can analyze data from smart meters, identify energy saving opportunities, and provide personalized recommendations to consumers.
The future of smart meters holds the promise of a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy future.
Regulatory Landscape and Policy Support for Smart Meter Deployment:
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in promoting smart meter deployment. Incentive programs, such as tax credits and rebates, can encourage utilities and consumers to invest in smart meters.
Regulatory frameworks that ensure data security and privacy are also essential for building consumer trust and promoting widespread adoption of smart meters. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, policymakers must stay abreast of emerging technologies and trends to develop effective regulations that support the growth of smart meter technology.
Conclusion
Smart meter deployment is transforming the way we use and manage energy. It offers numerous benefits, including improved energy efficiency, enhanced grid management, and enhanced customer service. However, challenges related to cost, privacy, and technical implementation need to be addressed.
By investing in smart meter technology, promoting collaborative efforts, and addressing these challenges, we can create a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy future.
For more information on electrical and plumbing products, visit **lichcupdienevn.com. Share your thoughts on smart meter deployment in the comments below, and don’t forget to share this article with your friends!
Đỗ Ngọc Hằng
