Understanding Electrical Power Meters: How They Work & Types Explained. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
How Electrical Power Meters Work
Think of an electrical power meter as a “meter reader” for your home’s electricity usage. It’s a device that measures the amount of electricity you use. But how does it do that?
The fundamental principle of electricity measurement relies on three key concepts:
- Voltage: This is the force that pushes electrons through a circuit, similar to the pressure in a water pipe.
- Current: This is the flow of electrons through a circuit, like the amount of water flowing through the pipe.
- Power: This is the rate at which energy is used or transferred, measured in watts. It’s like the amount of water flowing through the pipe per second.
Power meters work by measuring both voltage and current flowing through your electrical system. This data is then used to calculate the power consumption in watts. But what about energy consumption?
Energy consumption is the total amount of electricity used over a period of time, usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Power meters essentially track power consumption over time, providing the total energy used in kWh.
Now, let’s dive into the different types of power meters:
Types of Electrical Power Meters
There are three main types of electrical power meters:
- Analog Meters: These classic meters use an induction disc that rotates based on the current flowing through it. The speed of rotation is proportional to the amount of electricity used. A pointer attached to the disc indicates the usage on a graduated scale. Analog meters are simple and cost-effective, but they have limitations in accuracy and can be affected by external interference.
- Digital Meters: These meters utilize electronic sensors to measure voltage and current, displaying the information digitally. They are highly accurate and versatile, offering features like data logging and real-time monitoring. Digital meters can be more expensive than analog meters and may be susceptible to electronic failure.
- Smart Meters: These cutting-edge meters go beyond simply measuring your electricity consumption. They use wireless technology to communicate with the utility company, providing real-time data on your energy usage. This enables features like:
- Real-time monitoring: You can see exactly how much electricity you’re using at any given moment.
- Energy efficiency monitoring: Smart meters can help you identify areas where you can save energy by showing you your consumption patterns.
- Billing automation: Your bill can be calculated automatically based on your real-time usage data.
While smart meters have significant advantages, they also come with challenges such as:
* Privacy concerns: Data collected by smart meters can be sensitive, raising privacy concerns for some.
* Cybersecurity vulnerabilities: Like any connected device, smart meters are susceptible to cyberattacks, which could potentially compromise data security.
Reading Your Power Meter
Understanding how to read your power meter is essential for managing your energy consumption efficiently. The first step is to understand the display:
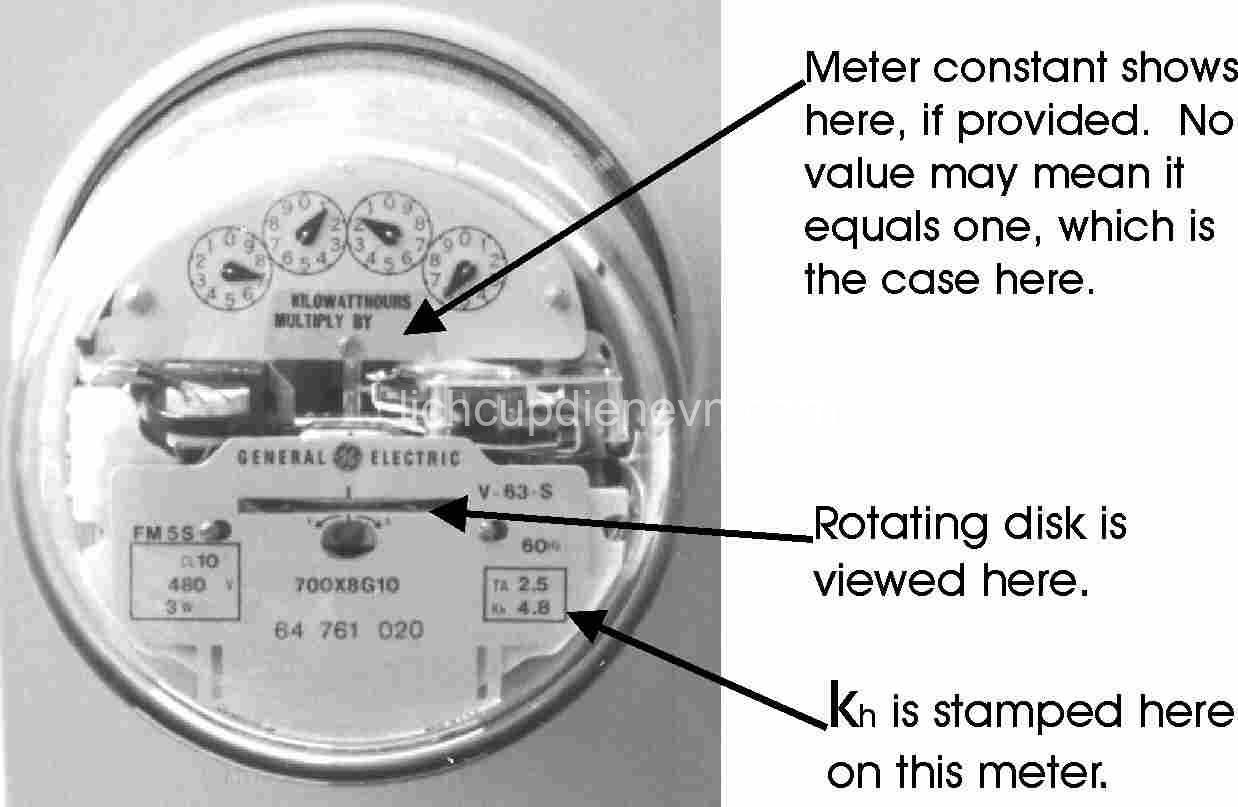
- Analog Meters: These typically have a series of dials with numbers or markings. To read an analog meter, you start from the rightmost dial and read the number that the pointer is closest to. Then, move to the next dial and repeat the process, reading the number closest to the pointer. Finally, multiply the readings together to get the total electricity consumption.
- Digital Meters: Digital meters display your electricity consumption directly in kWh. The numbers are usually clear and easy to understand.
Next, you need to understand the units of measurement:
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): This is the standard unit for measuring energy consumption. It represents the amount of energy used by a 1 kilowatt device running for one hour.
Managing Your Energy Consumption
Now that you know how to read your power meter, you can use that information to manage your energy consumption.
Here are some key factors that affect your power consumption:
- Appliances: Different appliances consume varying amounts of electricity. For example, a refrigerator uses more electricity than a light bulb.
- Lighting: Lighting can account for a significant portion of your electricity bill. Using energy-efficient light bulbs can help save energy.
- Seasonal Variations: Your electricity consumption may vary depending on the season. For example, you might use more electricity for heating in the winter and cooling in the summer.
- Time-of-Day: Some utility companies offer time-of-use rates, where electricity is more expensive during peak hours. By adjusting your electricity usage to off-peak hours, you can save money on your bill.
You can analyze your meter readings to identify patterns in your energy consumption:
- Track your usage: Keep a record of your meter readings over time to see how your electricity consumption changes.
- Analyze your bill: Your utility bill can provide insights into your energy usage patterns.
- Use data visualization tools: There are online tools and apps that can help you visualize your energy consumption data, making it easier to identify areas for improvement.
Once you understand your consumption patterns, you can use these strategies to save energy:
- Appliance Efficiency: Choose energy-efficient appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and dryers, with ENERGY STAR ratings.
- Energy-Saving Devices: Use power strips for electronics that aren’t in use, install programmable thermostats, and consider using smart plugs for appliances.
- Behavioral Changes: Unplug devices when not in use, turn off lights when leaving a room, and air dry clothes instead of using the dryer.
Importance of Accurate Meter Readings
Accurate meter readings are crucial for both your utility bill and energy efficiency:
- Accurate Billing: If your meter isn’t accurate, you could be overpaying for electricity or not paying enough. This can lead to financial difficulties or a strain on the electrical grid.
- Energy Efficiency: An inaccurate meter can make it difficult to track your energy usage and identify areas for improvement.
Here’s what you need to know about meter accuracy:
- Factors Affecting Accuracy: Several factors can impact the accuracy of your meter, such as its age, environmental conditions, and the presence of any interference.
- Meter Calibration: To ensure accuracy, meters are regularly calibrated. This involves testing the meter against a known standard to ensure it’s working properly.
- Regulatory Agencies: Regulatory agencies play a vital role in ensuring that meters are accurate and reliable. They set standards for meter accuracy and oversee the calibration process.
The Future of Power Meters: Smart Meter Technology
Smart meters are rapidly transforming the way we consume and manage electricity. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Real-time Energy Monitoring: Smart meters provide continuous updates on your energy usage, enabling you to see exactly how much electricity you’re using at any given moment. This information empowers you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
- Automated Billing: Smart meters can automatically send your usage data to the utility company, eliminating the need for manual meter readings and improving billing accuracy.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Smart meters can help support energy efficiency programs by providing real-time data that enables personalized feedback and recommendations.
Despite their benefits, smart meters also present some challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: The data collected by smart meters can be sensitive, raising privacy concerns for some individuals.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: As with any connected device, smart meters are susceptible to cyberattacks, which could potentially compromise data security.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Widespread adoption of smart meters requires significant infrastructure upgrades, which can be costly.
Resources and Further Exploration
For more information and to stay up-to-date on the latest in energy efficiency and power meter technology, I recommend exploring these resources:
- Utility Company Websites: Your local utility company website is a valuable source of information on meter readings, billing, and energy saving programs.
- Government Agencies and Non-Profit Organizations: Organizations such as the Department of Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency provide valuable resources on energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Online Tools: Numerous online tools and apps can help you calculate energy consumption, estimate savings, and track your usage patterns.
Don’t hesitate to explore these resources to further enhance your understanding of electrical power meters.
FAQs
What are the different types of power meters?
As previously discussed, the main types of power meters are analog meters, digital meters, and smart meters. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on your needs.
How often should I read my meter?
It’s recommended to read your meter at least once a month to track your energy consumption and identify any unusual fluctuations. This can help you pinpoint areas where you can save energy.
How do I know if my meter is accurate?
If you suspect your meter is inaccurate, contact your utility company. They can perform a meter test to determine if it’s working properly.
What are some ways to save energy at home?
There are numerous ways to save energy at home. Some of the most effective strategies include:
- Using energy-efficient appliances: Choose appliances with ENERGY STAR ratings, which are known for their efficiency.
- Installing programmable thermostats: Programmable thermostats can automatically adjust your heating and cooling systems to reduce energy consumption.
- Unplugging electronics when not in use: Electronics can consume energy even when they are turned off. Using power strips can help you easily unplug multiple devices at once.
- Turning off lights when leaving a room: This simple habit can make a significant impact on your energy consumption.
- Air drying clothes instead of using a dryer: Dryers are energy-intensive appliances. Line drying or using a clothes rack can help save energy and reduce your carbon footprint.
What are the benefits of smart meters?
Smart meters offer several benefits, including real-time energy monitoring, automated billing, and the ability to participate in energy efficiency programs. They provide valuable insights into your energy consumption patterns, helping you make informed decisions about your energy usage.
Conclusion
Understanding electrical power meters is crucial for managing your energy consumption efficiently and saving money on your electricity bill. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of meters, understanding how to read your meter, and implementing energy-saving strategies, you can make a positive impact on your energy usage and reduce your environmental footprint.
For more information on electricity, plumbing, and high-quality electrical and water products, visit my website at http://lichcupdienevn.com.
Don’t hesitate to share your thoughts and experiences with power meters in the comments section below. And remember, together, we can make a difference in managing our energy consumption for a sustainable future.
