Basic Electrical Wiring for Homes: Understanding Fundamentals & Circuits. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding the Fundamentals of Home Electrical Wiring
You might not think about electricity often, but it powers everything in your home. It’s important to have a basic understanding of how it works to keep your family safe and your home running smoothly.
Let’s start with the basics of electricity.
Electricity flows through a circuit, similar to water flowing through a pipe. The voltage is the pressure pushing the electricity through the circuit, like water pressure in a pipe. The current is the amount of electricity flowing, similar to the amount of water flowing in a pipe. Finally, resistance is how much the circuit opposes the flow of electricity, like a narrow pipe that slows down the water flow.
Understanding these three concepts is key to grasping how electricity works in your home.
Now let’s talk about some essential wiring components.
- Wires: Electricity flows through wires, which are typically insulated for safety. Romex and THHN are two common types of wires used in homes. Wires are color-coded to help identify their function, with black usually indicating hot wires, white for neutral wires, and green or bare copper for grounding wires.
- Circuit breakers: These devices protect your circuits from overload. If too much electricity flows through a circuit, the breaker will trip, interrupting the flow and preventing overheating or fire. They come in various amperage ratings, which indicate how much current they can safely handle.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): These specialized outlets are essential for safety, especially in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. They detect imbalances in electrical current and quickly shut off power to prevent electrical shocks.
- Outlets and switches: Outlets are the points where you plug in your appliances, while switches control the flow of electricity to lights and other devices. They come in different configurations depending on their purpose and electrical rating.
- Junction boxes: These enclosures hold the connections between wires. They are important for organizing wiring and ensuring safe electrical connections.
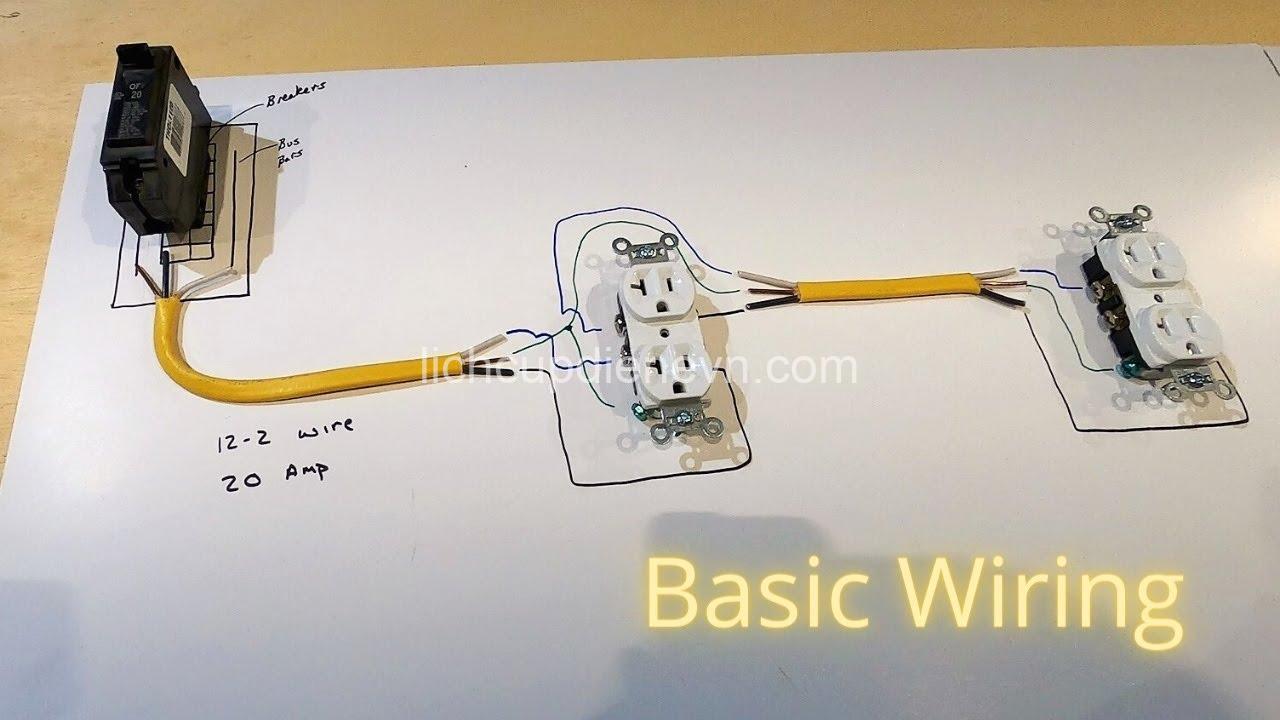
Basic Electrical Circuits for Homeowners
Now that you understand some of the essential components, let’s explore how they work together in electrical circuits.
There are two main types of circuits:
- Series circuits: In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other. Electricity must flow through each component to reach the end of the circuit. If one component breaks, the entire circuit is broken.
- Parallel circuits: In a parallel circuit, components are connected side-by-side. Electricity can flow through multiple paths, so if one component breaks, the others can still function.
Understanding the home electrical system:
The service panel is the central hub of your home’s electrical system. It contains the main breaker that controls the entire electrical supply to your house. The service panel also houses individual breakers for different circuits. Each breaker is connected to a specific circuit, and if that circuit overloads, the breaker will trip to protect it.
Common Home Electrical Wiring Tasks
Many simple electrical tasks can be tackled by homeowners with proper safety precautions and knowledge.
Replacing a Light Switch or Outlet:
- Safety First: Always turn off power to the circuit at the breaker box before working on any electrical components. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the power is off.
- Step-by-Step Process: Remove the cover plate of the switch or outlet. Carefully disconnect the wires from the old device, noting the color coding. Connect the wires to the new device according to the color coding. Secure the device to the electrical box and replace the cover plate.
- Troubleshooting: If the new switch or outlet doesn’t work, double-check the wiring connections and ensure the breaker is not tripped. If you are unsure, consult a professional electrician.
Adding a New Outlet or Light Fixture:
- Circuit Capacity: Make sure your existing circuit has enough capacity to handle the additional load before adding a new outlet or fixture.
- Running Wires: Running new wires through walls or ceilings requires careful planning and execution to avoid damage to existing wiring and structures.
- Wire Connections: Connecting wires to the new outlet or fixture involves carefully stripping the insulation, connecting wires according to color coding, and securing the connections.
Remember, safety should always be your top priority. If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical wiring, it’s best to consult a qualified electrician.
Electrical Safety in the Home
Electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. Always prioritize safety when working with electrical components.
Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Follow Electrical Codes: Always adhere to local electrical codes and safety regulations.
- Avoid Wet Areas: Never touch electrical components or appliances with wet hands.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools specifically designed for working with electricity.
- Be Cautious with Cords: Avoid overloading extension cords and inspect them regularly for damage.
When to Call a Professional Electrician:
It’s important to know your limitations and seek professional help when necessary. Here are some situations where you should call a licensed electrician:
- Complex Wiring Projects: Adding new circuits, upgrading electrical panels, or working with high-voltage systems.
- Electrical Problems: Experiencing frequent breaker trips, flickering lights, or shocks.
- Repairs in Wet Areas: Working with electrical components in bathrooms, kitchens, or outdoors.
Additional Resources for Learning More
If you’re interested in learning more about basic electrical wiring, there are many resources available online and in libraries. Here are some websites and books that you might find helpful:
- My Website: http://lichcupdienevn.com – Find helpful articles, videos, and product information on electrical systems and appliances.
Continuing Education:
Stay up-to-date on electrical codes, safety advancements, and new technologies by subscribing to industry publications or attending workshops.
Conclusion
Understanding basic electrical wiring can help you feel more confident about your home’s electrical system. Always prioritize safety, and consult a professional electrician when needed.
Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
Share this article with your friends and family!
Learn more about electrical systems and appliances on my website: http://lichcupdienevn.com
What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
In a series circuit, all components are connected in a single path, so electricity must flow through each component to complete the circuit. If one component fails, the entire circuit breaks. Think of a string of Christmas lights; if one bulb burns out, the whole string goes dark.
In a parallel circuit, components are connected side-by-side, allowing electricity to flow through multiple paths. If one component fails, the others can still function. Imagine a house with multiple light switches. You can turn on one light without affecting the others.
How do I know if a circuit is overloaded?
An overloaded circuit can be identified by several signs:
- Frequent Breaker Trips: If a breaker trips frequently, it could indicate that the circuit is overloaded.
- Dimming or Flickering Lights: Overloaded circuits can cause lights to dim or flicker.
- Warm Outlets or Switches: Overheating outlets or switches can be a sign of an overloaded circuit.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to reduce the load on the circuit or contact a professional electrician to evaluate the situation.
What is grounding and why is it important?
Grounding is a crucial safety feature in electrical systems. It provides a path for electricity to flow safely to the earth in case of a fault.
- Grounding Wire: The grounding wire is typically green or bare copper and is connected to the grounding rod driven into the earth.
- Ground Fault: If a fault occurs, such as a hot wire coming into contact with a metal enclosure, electricity can flow to the ground through the grounding wire, preventing a shock hazard.
Grounding is essential for protecting people and property from electrical hazards.
What are some common electrical problems and how can I troubleshoot them?
Here are some common electrical problems you might encounter in your home:
- Flickering Lights: Could be caused by loose connections, overloaded circuits, or faulty bulbs.
- Dead Outlets: Check the breaker to see if it has tripped, or inspect the outlet for loose connections or damage.
- Electrical Shock: This can be caused by a faulty appliance or a wiring issue. Immediately disconnect the appliance and consult a professional electrician.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems:
- Identify the Source: Is the problem affecting a single device or the entire circuit?
- Check the Breakers: Ensure the appropriate breaker is not tripped.
- Inspect Wires and Connections: Look for loose connections, damaged wires, or signs of overheating.
Remember, if you are unsure about any electrical issues, it’s always best to call a licensed electrician for assistance.
