Electricity Production Forecasts Amid Rising Demand: Challenges & Solutions. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Electricity Demand Trends and Forecasts
The world is increasingly reliant on electricity, and this dependence is only expected to grow in the coming years. Several factors contribute to this escalating demand, including population growth, urbanization, and economic development. As more people move to cities, and industries continue to expand, the need for reliable and affordable electricity will only become more critical.
Forecasting future electricity demand is a complex task, as it involves considering various factors such as economic growth, technological advancements, energy policies, and climate change impacts. Statistical models, econometric analysis, and energy system simulations are used to predict future demand, but these forecasts can be influenced by numerous uncertainties.
Global and regional demand projections point towards significant growth across various sectors, particularly in rapidly developing economies. However, these projections are subject to change, depending on factors like the pace of economic growth, the adoption of new technologies, and policy decisions.
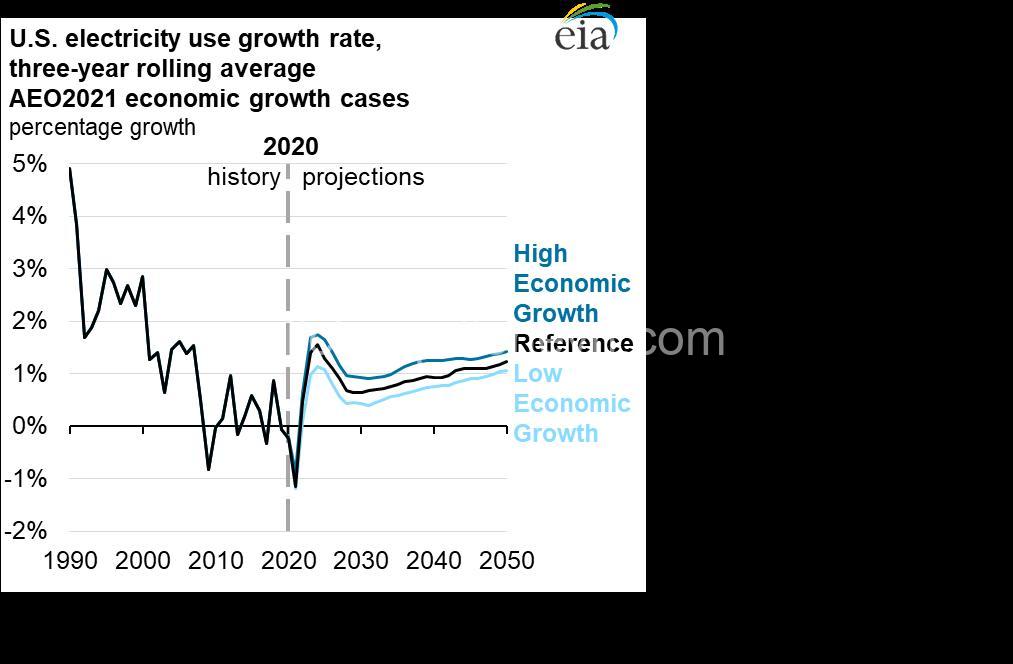
The Challenges of Meeting Rising Electricity Demand
While the demand for electricity continues to rise, meeting this growing need presents significant challenges. One of the primary concerns is infrastructure limitations. Existing power grids may struggle to handle the increased load, requiring modernization and expansion.
Furthermore, there are resource constraints. Limited availability of fossil fuels like coal and natural gas raises concerns about long-term energy security and environmental sustainability. Scaling up renewable energy sources like solar and wind power also faces challenges, such as land availability, intermittency, and storage.
Financial constraints pose another challenge. Investing in new generation capacity and grid infrastructure is expensive, requiring significant capital investment. Finding a balance between affordability and sustainability is crucial for making energy solutions accessible and feasible for all.
Finally, environmental concerns are a major factor. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from power generation is essential in mitigating climate change. Finding sustainable energy solutions that minimize environmental impact is a priority.
Strategies for Ensuring Adequate Electricity Supply
Addressing the challenges of rising electricity demand requires innovative solutions. Expanding renewable energy sources is a crucial step towards a sustainable energy future. Solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy offer clean and renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. Technological advancements and cost reductions in renewable energy have made them increasingly competitive.
Promoting energy efficiency plays a vital role in reducing electricity consumption. This involves implementing measures like improved building design, appliance standards, and encouraging energy-conscious behaviors. By reducing the overall demand for electricity, we can alleviate pressure on power grids and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Developing energy storage technologies is essential for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid. Technologies like batteries, pumped hydro, and compressed air energy storage allow for the storage of excess energy produced by renewables, ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply.
Grid modernization and smart grids are crucial for enhancing grid reliability, resilience, and efficiency. Digitalization and automation of power grids allow for better monitoring and control, enabling the integration of renewable energy and storage systems.
Demand-side management involves shifting electricity consumption to off-peak hours and incentivizing energy-efficient behaviors. By encouraging consumers to adjust their electricity usage, we can reduce strain on the power grid and minimize the need for new generation capacity.
The Role of Governments and Policymakers
Government policies and regulations play a critical role in shaping the future of electricity production and consumption. Energy policies can set targets for renewable energy deployment, implement carbon pricing mechanisms, and promote energy efficiency standards.
Investment in research and development is essential for advancing renewable energy technologies, grid modernization, and energy storage solutions. By supporting innovation, governments can accelerate the transition towards a clean and sustainable energy future.
International cooperation is crucial for sharing knowledge, best practices, and financial resources to support countries in their transition to clean energy. Collaborative efforts can accelerate the adoption of sustainable energy solutions and address global challenges related to climate change.
The Impact on Energy Security and Sustainability
Meeting rising electricity demand while ensuring energy security and environmental sustainability is a critical challenge. Energy security relies on reducing dependence on fossil fuels, diversifying energy sources, and building resilient energy systems.
Environmental sustainability requires reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting biodiversity, and minimizing water consumption. Finding energy solutions that address both energy security and environmental concerns is crucial for a sustainable future.
Balancing these competing priorities requires careful consideration of the trade-offs between different energy sources. Renewable energy sources offer a promising path towards a sustainable energy future, but their implementation requires careful planning and investment.
Key Players in the Electricity Production Landscape
Various players contribute to the electricity production landscape. Utilities and power generators play a crucial role in power generation, distribution, and transmission. They are responsible for investing in new technologies and infrastructure to meet rising electricity demand.
Renewable energy companies are dedicated to developing and deploying renewable energy projects, contributing to the shift towards a clean energy future. They are driving innovation in renewable energy technologies and expanding the adoption of sustainable energy solutions.
Technology providers offer solutions for grid modernization, energy storage, and smart grids, enabling the integration of renewable energy and the development of more efficient and resilient energy systems.
Consumers play a vital role in driving demand for clean and affordable electricity. They can contribute to sustainability by adopting energy-efficient technologies and participating in demand-side management programs.
The Future of Electricity Production Forecasts
Advancements in data analytics and artificial intelligence are transforming how we forecast electricity demand. These tools are improving the accuracy and reliability of forecasts, enabling better planning and decision-making for the future of energy production.
Emerging technologies such as hydrogen energy, nuclear fusion, and other innovative solutions hold promise for the future of electricity production. These technologies have the potential to further reduce emissions, enhance energy security, and provide new avenues for meeting the world’s growing energy needs.
The role of digitalization and automation is expanding in the electricity sector. These technologies are optimizing grid operations, improving energy management, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy and storage systems.
The future of electricity production depends on continued research and development. Exploring new technologies and solutions is crucial for addressing the challenges of meeting rising electricity demand while promoting sustainability.
What are the major factors driving electricity demand growth?
The major factors driving electricity demand growth are:
- Population growth and urbanization: As populations grow and more people move to cities, the demand for electricity increases to meet the needs of residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
- Economic development and industrialization: Growing economies and industrial expansion require more electricity to power factories, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Electrification of transportation: The adoption of electric vehicles, which run on electricity, is driving demand for electricity in the transportation sector.
What are the main challenges in meeting rising electricity demand?
Meeting rising electricity demand poses several challenges:
- Infrastructure limitations: Existing power grids may not have the capacity to handle increased demand, requiring investment in grid modernization and expansion.
- Resource constraints: Limited availability of fossil fuels and the challenges in scaling up renewable energy sources can create difficulties in meeting the growing need for electricity.
- Financial constraints: Investing in new generation capacity, grid infrastructure, and renewable energy technologies requires significant financial resources.
- Environmental concerns: The need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize environmental impact adds complexity to the challenge of meeting rising electricity demand.
What are the key strategies for ensuring adequate electricity supply?
Strategies for ensuring adequate electricity supply include:
- Expanding renewable energy sources: Investing in solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Promoting energy efficiency: Implementing measures to reduce electricity consumption through building retrofits, appliance standards, and behavioral changes.
- Developing energy storage technologies: Investing in technologies like batteries, pumped hydro, and compressed air energy storage to improve the reliability of renewable energy sources.
- Grid modernization and smart grids: Upgrading power grids with digitalization and automation to enhance reliability, resilience, and efficiency.
- Demand-side management: Encouraging consumers to shift electricity consumption to off-peak hours and adopt energy-efficient behaviors.
What are the roles of governments and policymakers in addressing electricity demand growth?
Governments and policymakers play a vital role in addressing electricity demand growth by:
- Setting energy policies and regulations: Establishing targets for renewable energy deployment, implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, and promoting energy efficiency standards.
- Investing in research and development: Funding innovation in renewable energy technologies, grid modernization, and energy storage solutions.
- Promoting international cooperation: Sharing knowledge, best practices, and financial resources to support countries in their transition to clean energy.
How can consumers contribute to meeting rising electricity demand?
Consumers can contribute to meeting rising electricity demand by:
- Adopting energy-efficient appliances and technologies: Choosing energy-efficient products for their homes and businesses.
- Participating in demand-side management programs: Adjusting their energy consumption to off-peak hours and adopting energy-saving habits.
- Supporting renewable energy projects: Choosing renewable energy providers or investing in solar panels for their homes.
- Advocating for sustainable energy policies: Engaging in policy discussions and supporting initiatives that promote clean and renewable energy.
Conclusion
The world is facing a significant challenge in meeting rising electricity demand while ensuring energy security and environmental sustainability. By understanding the trends and challenges, exploring innovative solutions, and embracing collaboration, we can create a more sustainable and secure energy future.
For more information on energy efficiency, renewable energy, and sustainable solutions, visit lichcupdienevn.com. We encourage you to share your thoughts on this topic by leaving a comment below. You can also stay updated on the latest trends in electricity and water by subscribing to our website and sharing our content with your friends and family.
EAVs (Entity – Attribute – Value):
- Electricity Production – Source – Coal
- Electricity Production – Source – Natural Gas
- Electricity Production – Source – Renewable Energy
- Electricity Production – Source – Nuclear Energy
- Demand – Sector – Residential
- Demand – Sector – Commercial
- Demand – Sector – Industrial
- Forecasts – Methodology – Statistical Modeling
- Forecasts – Methodology – Econometric Analysis
- Forecasts – Methodology – Energy System Simulation
- Renewable Energy – Type – Solar
- Renewable Energy – Type – Wind
- Renewable Energy – Type – Hydropower
- Energy Storage – Technology – Batteries
- Energy Storage – Technology – Pumped Hydro
- Energy Storage – Technology – Compressed Air Energy Storage
- Grid Modernization – Feature – Smart Grids
- Grid Modernization – Feature – Microgrids
- Energy Efficiency – Measure – Building Retrofits
- Energy Efficiency – Measure – Appliance Standards
ERE (Entity, Relation, Entity):
- Electricity Production – Depends On – Resources
- Demand – Influenced By – Economic Growth
- Forecasts – Based On – Data Analysis
- Renewable Energy – Contributes To – Energy Supply
- Energy Storage – Improves – Grid Stability
- Grid Modernization – Facilitates – Integration Of Renewables
- Energy Efficiency – Reduces – Electricity Consumption
- Climate Change – Impacts – Electricity Demand
- Government Policy – Shapes – Electricity Production
- Consumers – Drive – Demand
- Technology – Enables – Renewable Energy Growth
- Investments – Fund – Infrastructure Development
- Power Plants – Generate – Electricity
- Utilities – Distribute – Electricity
- Businesses – Rely On – Electricity
- Industries – Consume – Electricity
- Researchers – Develop – New Technologies
- Environmental Groups – Advocate For – Sustainability
- Investors – Seek – Profitability
- Regulators – Ensure – Safety and Reliability
Semantic Triples (Subject, Predicate, Object):
- (Electricity Production, Is Driven By, Rising Demand)
- (Forecasts, Are Based On, Data Analysis)
- (Renewable Energy, Contributes To, Energy Security)
- (Energy Storage, Improves, Grid Reliability)
- (Grid Modernization, Facilitates, Integration Of Renewables)
- (Energy Efficiency, Reduces, Electricity Consumption)
- (Climate Change, Impacts, Electricity Demand)
- (Government Policy, Shapes, Electricity Production)
- (Consumers, Drive, Demand)
- (Technology, Enables, Renewable Energy Growth)
- (Investments, Fund, Infrastructure Development)
- (Power Plants, Generate, Electricity)
- (Utilities, Distribute, Electricity)
- (Businesses, Rely On, Electricity)
- (Industries, Consume, Electricity)
- (Researchers, Develop, New Technologies)
- (Environmental Groups, Advocate For, Sustainability)
- (Investors, Seek, Profitability)
- (Regulators, Ensure, Safety and Reliability)
- (Electricity, Is Essential For, Economic Growth)
