Understanding Electrical Insulation Resistance: Importance & Measurement. In today’s article, lichcupdienevn.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
What is Electrical Insulation Resistance and Why is it Important?
Electrical insulation is like a protective barrier around electrical wires and components, preventing dangerous electric currents from escaping. Imagine it as a rubber coating on a wire, keeping the electricity contained and flowing where it’s supposed to. Electrical insulation resistance measures how effectively this insulation prevents current leakage. It essentially tells you how well the insulation is doing its job.
Why is this crucial? Imagine a faulty wire with damaged insulation. Electricity could leak out, potentially causing electric shock or even starting a fire. Electrical insulation resistance testing helps identify such issues before they become dangerous. By ensuring proper insulation resistance, you’re protecting yourself, your family, and your property from electrical hazards.
It’s like having a safety net for your electrical system. A good insulation resistance means a more reliable and efficient system, preventing breakdowns and ensuring a longer lifespan for your electrical appliances.
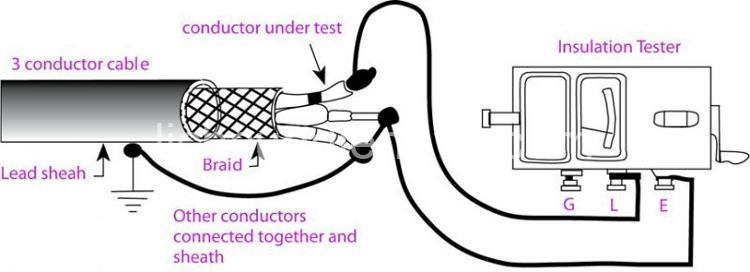
How to Measure Insulation Resistance
The most common tool for measuring insulation resistance is a Megger tester. It works by applying a high voltage to the insulation and then measuring the amount of current that leaks through. It’s like checking for cracks in the protective barrier.
Megger testers come in different types, each suited for specific applications. Some are analog, with a needle that moves across a scale, while others are digital, displaying the readings on a screen.
There are also other testing methods like the HiPot test, which is used for larger systems or components with high voltage requirements.
Factors Affecting Insulation Resistance
Electrical insulation resistance is not a fixed value. It can be affected by various factors, including the material properties, environment, and even time:
Material Properties:
- Dielectric strength is like the strength of the insulation material. A material with higher dielectric strength can withstand a higher voltage before breaking down.
- Resistivity measures the material’s ability to resist the flow of electricity. Higher resistivity means better insulation.
- Moisture content: Moisture can penetrate insulation materials, reducing their resistance and making them more prone to leakage.
Environmental Factors:
- Temperature: Extreme heat can degrade insulation, reducing its effectiveness.
- Humidity: High humidity can promote moisture absorption, lowering insulation resistance.
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, oil, and other contaminants can accumulate on insulation, creating pathways for current leakage.
Aging and Degradation:
- Over time, insulation materials can age and deteriorate, leading to reduced resistance.
- Physical damage, such as cuts or tears, can also compromise insulation and lower resistance.
Applications of Insulation Resistance Testing
Insulation resistance testing is essential in various industries to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Some key applications include:
- Power generation and distribution: Regular testing of power cables, transformers, and other equipment ensures they function correctly and safely.
- Industrial equipment: Testing motors, generators, and control systems is crucial for safe operation and optimal performance.
- Electronics and instrumentation: Insulation resistance testing is vital for sensitive electronic devices and measurement instruments.
- Telecommunications: Ensuring the reliability of telecommunications infrastructure, including cables and switching equipment, is paramount.
- Building and infrastructure: Regular testing of electrical installations in buildings and infrastructure is crucial for safety and functionality.
Imagine a power plant or a major industrial facility. Imagine the consequences of a power failure or an equipment malfunction caused by faulty insulation. It’s a scenario that no one wants to face, and insulation resistance testing helps prevent such situations.
Best Practices for Insulation Resistance Testing
Insulation resistance testing should be carried out by qualified professionals, ensuring proper procedures and adherence to industry standards. Key best practices include:
- Test voltage selection: The test voltage must be appropriate for the type of insulation and the rated voltage of the equipment.
- Testing procedures: Following established procedures ensures accuracy and consistency in testing results.
- Result interpretation: Understanding the test readings and interpreting their meaning is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Record-keeping: Maintaining accurate records of insulation resistance testing provides valuable data for future analysis and maintenance planning.
Conclusion
Understanding electrical insulation resistance is essential for anyone involved in electrical systems. By regularly testing and maintaining insulation, you’re not only ensuring the safety of yourself and your property but also ensuring the reliability and longevity of your electrical equipment.
For more information and resources on electrical insulation resistance and other electrical safety topics, visit my website at http://lichcupdienevn.com. As an electrical and plumbing expert, I’m committed to providing valuable knowledge and resources to help you make informed decisions about your electrical and plumbing needs.
Let’s continue the conversation! Leave a comment below to share your thoughts, ask questions, or share your own experiences with electrical insulation resistance. Don’t forget to share this article with others who might find it helpful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the units of measurement for insulation resistance?
Insulation resistance is measured in ohms. The higher the resistance value, the better the insulation quality.
What is the relationship between insulation resistance and leakage current?
Leakage current is the current that flows through the insulation material, indicating a fault in the insulation. Insulation resistance is inversely proportional to leakage current. This means higher resistance means lower leakage current, indicating better insulation.
What are the typical values for insulation resistance in electrical systems?
The acceptable values for insulation resistance vary depending on the type of equipment and its rated voltage. Generally, values of a few megaohms or higher are considered good.
How often should insulation resistance testing be performed?
The frequency of insulation resistance testing depends on the type of equipment and its operating environment. Some equipment might require testing daily or weekly, while others might require testing only annually.
What happens when insulation resistance falls below acceptable levels?
If the insulation resistance falls below the acceptable level, it indicates a potential fault in the insulation. This could lead to electrical hazards, equipment failure, and safety risks.
EAV (Entity – Attribute – Value)
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Unit, Value: Ohm
- Entity: Megger Tester, Attribute: Type, Value: Analog, Digital
- Entity: HiPot Test, Attribute: Voltage, Value: High voltage
- Entity: Dielectric Material, Attribute: Type, Value: Polypropylene, PVC, Teflon
- Entity: Leakage Current, Attribute: Unit, Value: Microampere
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Measurement Method, Value: Megger, HiPot
- Entity: Dielectric Strength, Attribute: Unit, Value: Volts per mil
- Entity: Electrical Equipment, Attribute: Application, Value: Motors, Transformers, Generators
- Entity: Safety Regulation, Attribute: Standard, Value: IEC 60034, IEEE 43
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Temperature, Value: Decreases with increasing temperature
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Humidity, Value: Decreases with increasing humidity
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Contamination, Value: Decreases with contamination
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Age, Value: Decreases with age
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Degradation, Value: Decreases with degradation
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Mechanical Stress, Value: Decreases with mechanical stress
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Attribute: Impact of Damage, Value: Decreases with damage
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Attribute: Purpose, Value: Preventative maintenance, Troubleshooting
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Attribute: Importance, Value: Safety, Reliability, Performance
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Attribute: Applications, Value: Power generation, Industrial equipment, Electronics
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Attribute: Standards, Value: IEC 60034, IEEE 43
ERE (Entity, Relation, Entity)
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Measured by, Entity: Megger Tester
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Affected by, Entity: Dielectric Material
- Entity: Megger Tester, Relation: Used for, Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing
- Entity: Dielectric Material, Relation: Determines, Entity: Dielectric Strength
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Influenced by, Entity: Temperature
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Influenced by, Entity: Humidity
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Influenced by, Entity: Contamination
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Affected by, Entity: Age
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Affected by, Entity: Degradation
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Affected by, Entity: Mechanical Stress
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Affected by, Entity: Damage
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Relation: Ensures, Entity: Safety
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Relation: Improves, Entity: Reliability
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Relation: Used in, Entity: Preventive Maintenance
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Relation: Used in, Entity: Troubleshooting
- Entity: Insulation Resistance Testing, Relation: Performed on, Entity: Electrical Equipment
- Entity: Electrical Equipment, Relation: Has, Entity: Insulation
- Entity: Insulation, Relation: Provides, Entity: Electrical Isolation
- Entity: Insulation Resistance, Relation: Indicates, Entity: Electrical Isolation Effectiveness
- Entity: Leakage Current, Relation: Flows through, Entity: Insulation
Semantic Triple (Subject, Predicate, Object):
- Subject: Insulation resistance, Predicate: Is a measure of, Object: Electrical isolation effectiveness
- Subject: Megger tester, Predicate: Used for, Object: Measuring insulation resistance
- Subject: HiPot test, Predicate: Applies, Object: High voltage to insulation
- Subject: Dielectric strength, Predicate: Represents, Object: Ability of a material to withstand electrical stress
- Subject: Leakage current, Predicate: Flows, Object: Through insulation
- Subject: Temperature, Predicate: Affects, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Humidity, Predicate: Affects, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Contamination, Predicate: Reduces, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Age, Predicate: Decreases, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Degradation, Predicate: Affects, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Mechanical stress, Predicate: Affects, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Damage, Predicate: Affects, Object: Insulation resistance
- Subject: Insulation resistance testing, Predicate: Helps, Object: Prevent electrical failures
- Subject: Insulation resistance testing, Predicate: Used for, Object: Preventive maintenance
- Subject: Insulation resistance testing, Predicate: Used for, Object: Troubleshooting
- Subject: Insulation resistance, Predicate: Important for, Object: Electrical safety
- Subject: Insulation resistance, Predicate: Important for, Object: Equipment reliability
- Subject: Insulation resistance, Predicate: Measured in, Object: Ohms
- Subject: Insulation resistance testing, Predicate: Performed according to, Object: Industry standards
- Subject: Insulation resistance, Predicate: Can be, Object: Affected by environmental factors
